About ASpdb
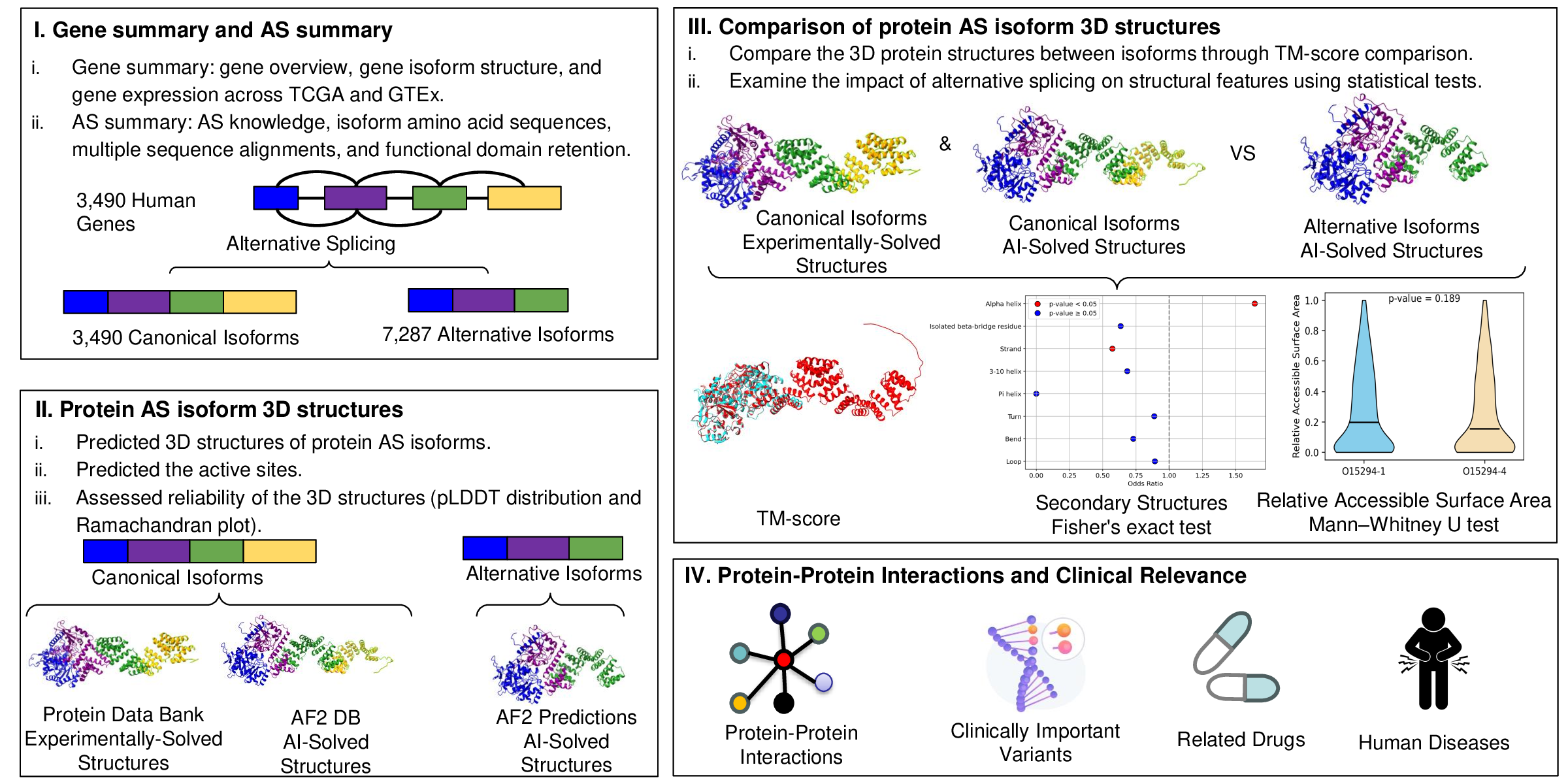
Alternative splicing is an important cellular process in eukaryotes, altering pre-mRNA to yield multiple protein isoforms from a single gene. To enhance our understanding of the impact of alternative splicing events on protein structures, we employed AlphaFold 2, a cutting-edge protein structure prediction tool, to comprehensively analyze alternative splicing for 3,400 human genes (more than 3,400 canonical isoforms and more than 7,400 alternative isoforms). ASpdb offers a user-friendly platform to access a wealth of information on human alternative splicing, including detailed protein structure data, sequence variations, structural attributes, and functional annotations. We also performed comparative analyses of structural alterations between canonical and alternative isoforms post-splicing, providing insights into their potential biological impacts. Our diverse analyses released through ASpdb will shed light on the identification of the relationships between alternative splicing, evolution, and human disease.
Please cite:
Yuntao Yang, Himansu Kumar, Yuhan Xie, Zhao Li, Rongbin Li, Wenbo Chen, Chiamaka S Diala, Meer A Ali, Yi Xu, Albon Wu, Sayed-Rzgar Hosseini, Erfei Bi, Hongyu Zhao, Pora Kim, W Jim Zheng: ASpdb: an integrative knowledgebase of human protein isoforms from experimental and AI-predicted structures, Nucleic Acids Research, 53(D1):D331-339, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkae1018
| 

 Search
Search Browse by important cellular gene groups
Browse by important cellular gene groups Browse by Drug target group
Browse by Drug target group