Protein:CD209 |
Protein Summary |
 Gene summary Gene summary |
| Gene name: CD209 | ASpdb.0 ID: 30835 | Gene | Gene symbol | CD209 | Gene ID | 30835 |
| Gene name | CD209 molecule |
| Synonyms | CDSIGN|CLEC4L|DC-SIGN|DC-SIGN1|hDC-SIGN |
| Cytomap | 19p13.2 |
| Type of gene | protein-coding |
| Description | CD209 antigenC-type lectin domain family 4 member LHIV gpl20-binding proteindendritic cell-specific ICAM-3-grabbing non-integrin 1dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-3-grabbing non-integrindendritic cell-specific intracellular adh |
| Modification date | 20240305 |
| UniProtAcc | Q9NNX6 |
 Gene ontology of this gene with evidence of Inferred from Direct Assay (IDA) from Entrez Gene ontology of this gene with evidence of Inferred from Direct Assay (IDA) from Entrez |
| Partner | Gene | GO ID | GO term | PubMed ID |
| Gene | CD209 | GO:0001618 | virus receptor activity | 22156524|24623090 |
| Gene | CD209 | GO:0005886 | plasma membrane | 12421943 |
| Gene | CD209 | GO:0009897 | external side of plasma membrane | 24942581 |
| Gene | CD209 | GO:0042102 | positive regulation of T cell proliferation | 12421943 |
| Gene | CD209 | GO:0042129 | regulation of T cell proliferation | 12456590 |
| Gene | CD209 | GO:0046718 | symbiont entry into host cell | 24623090 |
| Gene | CD209 | GO:0097323 | B cell adhesion | 12421943 |
AS Summary |
 Information of the canonical protein with experimentally identified structure from PDB (2023). Information of the canonical protein with experimentally identified structure from PDB (2023). |
| UniProt Acc | File name | PDB ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Start | End |
| Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-1_6ghv_C.pdb | 6GHV | X-ray | 2.1 | C | 252 | 384 |
 ASpdb's canonical and alternatively spliced isoform information. ASpdb's canonical and alternatively spliced isoform information. |
| accession_id | gene_name | canonical_id | alternative_id | canonical_length | alternative_length | canonical_start | canonical_end | type | originalSEQ | variationSEQ | alternative_start | alternative_end |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-10 | 404 | 380 | 1 | 15 | Substitution | MSDSKEPRLQQLGLL | MASACPGSDFTSIHS | 1 | 15 |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-10 | 404 | 380 | 36 | 59 | Deletion | none | none | 35 | 35 |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-11 | 404 | 334 | 1 | 15 | Substitution | MSDSKEPRLQQLGLL | MASACPGSDFTSIHS | 1 | 15 |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-11 | 404 | 334 | 36 | 59 | Deletion | none | none | 35 | 35 |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-11 | 404 | 334 | 191 | 236 | Deletion | none | none | 166 | 166 |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-12 | 404 | 297 | 1 | 15 | Substitution | MSDSKEPRLQQLGLL | MASACPGSDFTSIHS | 1 | 15 |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-12 | 404 | 297 | 36 | 59 | Deletion | none | none | 35 | 35 |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-12 | 404 | 297 | 301 | 321 | Substitution | NFLQLQSSRSNRFTWMGLSDL | LQAVLEQRRAQQRWGGRLRGI | 277 | 297 |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-12 | 404 | 297 | 322 | 404 | Deletion | none | none | 297 | 297 |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-2 | 404 | 398 | 301 | 306 | Deletion | none | none | 300 | 300 |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-3 | 404 | 312 | 158 | 249 | Deletion | none | none | 157 | 157 |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-4 | 404 | 168 | 74 | 309 | Deletion | none | none | 73 | 73 |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-5 | 404 | 404 | 1 | 15 | Substitution | MSDSKEPRLQQLGLL | MASACPGSDFTSIHS | 1 | 15 |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-6 | 404 | 380 | 36 | 59 | Deletion | none | none | 35 | 35 |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-7 | 404 | 360 | 16 | 59 | Deletion | none | none | 15 | 15 |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-8 | 404 | 268 | 16 | 59 | Deletion | none | none | 15 | 15 |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-8 | 404 | 268 | 142 | 233 | Deletion | none | none | 97 | 97 |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-9 | 404 | 34 | 30 | 34 | Substitution | GYKSL | RNQKC | 30 | 34 |
| Q9NNX6 | CD209 | Q9NNX6-1 | Q9NNX6-9 | 404 | 34 | 35 | 404 | Deletion | none | none | 34 | 34 |
 Multiple sequence alignment of our canonical and alternatively spliced CD209 Multiple sequence alignment of our canonical and alternatively spliced CD209 |
 Matched gene isoform IDs with Ensembl and RefSeq of our canonical and alternative spliced genes of CD209 Matched gene isoform IDs with Ensembl and RefSeq of our canonical and alternative spliced genes of CD209 |
| UniProt-id | ENSG | ENST | ENSP |
| Q9NNX6-1 | ENSG00000090659.18 | ENST00000315599.12 | ENSP00000315477.6 |
| Q9NNX6-10 | ENSG00000090659.18 | ENST00000601951.5 | ENSP00000468827.1 |
| Q9NNX6-12 | ENSG00000090659.18 | ENST00000601256.1 | ENSP00000470658.1 |
| Q9NNX6-2 | ENSG00000090659.18 | ENST00000354397.10 | ENSP00000346373.5 |
| Q9NNX6-3 | ENSG00000090659.18 | ENST00000602261.5 | ENSP00000471137.1 |
| Q9NNX6-4 | ENSG00000090659.18 | ENST00000394161.9 | ENSP00000377716.4 |
| Q9NNX6-6 | ENSG00000090659.18 | ENST00000315591.12 | ENSP00000315407.7 |
| Q9NNX6-7 | ENSG00000090659.18 | ENST00000204801.12 | ENSP00000204801.7 |
| UniProt-id | NM ID | NP ID |
| Q9NNX6-1 | NM_021155.3 | NP_066978.1 |
| Q9NNX6-2 | NM_001144897.1 | NP_001138369.1 |
| Q9NNX6-3 | NM_001144895.1 | NP_001138367.1 |
| Q9NNX6-6 | NM_001144896.1 | NP_001138368.1 |
| Q9NNX6-7 | NM_001144894.1 | NP_001138366.1 |
 Amino acid sequences of our canonical and alternatively spliced CD209 Amino acid sequences of our canonical and alternatively spliced CD209 |
| accession_id | Protein sequence |
| Q9NNX6-1 | MSDSKEPRLQQLGLLEEEQLRGLGFRQTRGYKSLAGCLGHGPLVLQLLSFTLLAGLLVQVSKVPSSISQEQSRQDAIYQNLTQLKAAVGE LSEKSKLQEIYQELTQLKAAVGELPEKSKLQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKLQEIYQELTWLKAAVGELPEKSKMQEIYQELTRLKAAV GELPEKSKQQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKQQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKQQEIYQELTQLKAAVERLCHPCPWEWTFFQGNCYFM SNSQRNWHDSITACKEVGAQLVVIKSAEEQNFLQLQSSRSNRFTWMGLSDLNQEGTWQWVDGSPLLPSFKQYWNRGEPNNVGEEDCAEFS |
| Q9NNX6-10 | MASACPGSDFTSIHSEEEQLRGLGFRQTRGYKSLAVSKVPSSISQEQSRQDAIYQNLTQLKAAVGELSEKSKLQEIYQELTQLKAAVGEL PEKSKLQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKLQEIYQELTWLKAAVGELPEKSKMQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKQQEIYQELTRLKAAVG ELPEKSKQQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKQQEIYQELTQLKAAVERLCHPCPWEWTFFQGNCYFMSNSQRNWHDSITACKEVGAQLVVI KSAEEQNFLQLQSSRSNRFTWMGLSDLNQEGTWQWVDGSPLLPSFKQYWNRGEPNNVGEEDCAEFSGNGWNDDKCNLAKFWICKKSAASC |
| Q9NNX6-11 | MASACPGSDFTSIHSEEEQLRGLGFRQTRGYKSLAVSKVPSSISQEQSRQDAIYQNLTQLKAAVGELSEKSKLQEIYQELTQLKAAVGEL PEKSKLQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKLQEIYQELTWLKAAVGELPEKSKMQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKQQEIYQELTQLKAAVE RLCHPCPWEWTFFQGNCYFMSNSQRNWHDSITACKEVGAQLVVIKSAEEQNFLQLQSSRSNRFTWMGLSDLNQEGTWQWVDGSPLLPSFK |
| Q9NNX6-12 | MASACPGSDFTSIHSEEEQLRGLGFRQTRGYKSLAVSKVPSSISQEQSRQDAIYQNLTQLKAAVGELSEKSKLQEIYQELTQLKAAVGEL PEKSKLQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKLQEIYQELTWLKAAVGELPEKSKMQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKQQEIYQELTRLKAAVG ELPEKSKQQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKQQEIYQELTQLKAAVERLCHPCPWEWTFFQGNCYFMSNSQRNWHDSITACKEVGAQLVVI |
| Q9NNX6-2 | MSDSKEPRLQQLGLLEEEQLRGLGFRQTRGYKSLAGCLGHGPLVLQLLSFTLLAGLLVQVSKVPSSISQEQSRQDAIYQNLTQLKAAVGE LSEKSKLQEIYQELTQLKAAVGELPEKSKLQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKLQEIYQELTWLKAAVGELPEKSKMQEIYQELTRLKAAV GELPEKSKQQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKQQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKQQEIYQELTQLKAAVERLCHPCPWEWTFFQGNCYFM SNSQRNWHDSITACKEVGAQLVVIKSAEEQSSRSNRFTWMGLSDLNQEGTWQWVDGSPLLPSFKQYWNRGEPNNVGEEDCAEFSGNGWND |
| Q9NNX6-3 | MSDSKEPRLQQLGLLEEEQLRGLGFRQTRGYKSLAGCLGHGPLVLQLLSFTLLAGLLVQVSKVPSSISQEQSRQDAIYQNLTQLKAAVGE LSEKSKLQEIYQELTQLKAAVGELPEKSKLQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKLQEIYQELTWLKAAVERLCHPCPWEWTFFQGNCYFMSN SQRNWHDSITACKEVGAQLVVIKSAEEQNFLQLQSSRSNRFTWMGLSDLNQEGTWQWVDGSPLLPSFKQYWNRGEPNNVGEEDCAEFSGN |
| Q9NNX6-4 | MSDSKEPRLQQLGLLEEEQLRGLGFRQTRGYKSLAGCLGHGPLVLQLLSFTLLAGLLVQVSKVPSSISQEQSRSNRFTWMGLSDLNQEGT |
| Q9NNX6-5 | MASACPGSDFTSIHSEEEQLRGLGFRQTRGYKSLAGCLGHGPLVLQLLSFTLLAGLLVQVSKVPSSISQEQSRQDAIYQNLTQLKAAVGE LSEKSKLQEIYQELTQLKAAVGELPEKSKLQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKLQEIYQELTWLKAAVGELPEKSKMQEIYQELTRLKAAV GELPEKSKQQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKQQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKQQEIYQELTQLKAAVERLCHPCPWEWTFFQGNCYFM SNSQRNWHDSITACKEVGAQLVVIKSAEEQNFLQLQSSRSNRFTWMGLSDLNQEGTWQWVDGSPLLPSFKQYWNRGEPNNVGEEDCAEFS |
| Q9NNX6-6 | MSDSKEPRLQQLGLLEEEQLRGLGFRQTRGYKSLAVSKVPSSISQEQSRQDAIYQNLTQLKAAVGELSEKSKLQEIYQELTQLKAAVGEL PEKSKLQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKLQEIYQELTWLKAAVGELPEKSKMQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKQQEIYQELTRLKAAVG ELPEKSKQQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKQQEIYQELTQLKAAVERLCHPCPWEWTFFQGNCYFMSNSQRNWHDSITACKEVGAQLVVI KSAEEQNFLQLQSSRSNRFTWMGLSDLNQEGTWQWVDGSPLLPSFKQYWNRGEPNNVGEEDCAEFSGNGWNDDKCNLAKFWICKKSAASC |
| Q9NNX6-7 | MSDSKEPRLQQLGLLVSKVPSSISQEQSRQDAIYQNLTQLKAAVGELSEKSKLQEIYQELTQLKAAVGELPEKSKLQEIYQELTRLKAAV GELPEKSKLQEIYQELTWLKAAVGELPEKSKMQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKQQEIYQELTRLKAAVGELPEKSKQQEIYQELTRLKA AVGELPEKSKQQEIYQELTQLKAAVERLCHPCPWEWTFFQGNCYFMSNSQRNWHDSITACKEVGAQLVVIKSAEEQNFLQLQSSRSNRFT WMGLSDLNQEGTWQWVDGSPLLPSFKQYWNRGEPNNVGEEDCAEFSGNGWNDDKCNLAKFWICKKSAASCSRDEEQFLSPAPATPNPPPA |
| Q9NNX6-8 | MSDSKEPRLQQLGLLVSKVPSSISQEQSRQDAIYQNLTQLKAAVGELSEKSKLQEIYQELTQLKAAVGELPEKSKLQEIYQELTRLKAAV GELPEKSKQQEIYQELTQLKAAVERLCHPCPWEWTFFQGNCYFMSNSQRNWHDSITACKEVGAQLVVIKSAEEQNFLQLQSSRSNRFTWM |
| Q9NNX6-9 |
Protein Functional Features |
 Main function of this protein. (from UniProt) Main function of this protein. (from UniProt) |
| CD209 (go to UniProt):Q9NNX6 |
 Retention analysis result of protein across 39 protein features of UniProt such as six molecule processing features, 13 region features, four site features, six amino acid modification features, two natural variation features, five experimental info features, and 3 secondary structure features. Here, because of limited space for viewing, we only show the protein feature retention information belong to the 13 regional features. All retention annotation result can be downloaded at * Minus value of BPloci means that the break pointn is located before the CDS. Retention analysis result of protein across 39 protein features of UniProt such as six molecule processing features, 13 region features, four site features, six amino acid modification features, two natural variation features, five experimental info features, and 3 secondary structure features. Here, because of limited space for viewing, we only show the protein feature retention information belong to the 13 regional features. All retention annotation result can be downloaded at * Minus value of BPloci means that the break pointn is located before the CDS. |
| - Retained protein feature among the 13 regional features. |
| Accession_id | Subsection | Start | End | Funcitonal feature | Splicing information |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 1 | 37 | Note=Cytoplasmic;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Substitution;Start=1;End=15 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 1 | 37 | Note=Cytoplasmic;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=36;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 1 | 37 | Note=Cytoplasmic;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Substitution;Start=1;End=15 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 1 | 37 | Note=Cytoplasmic;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=36;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 1 | 37 | Note=Cytoplasmic;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Substitution;Start=1;End=15 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 1 | 37 | Note=Cytoplasmic;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=36;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 1 | 37 | Note=Cytoplasmic;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Substitution;Start=1;End=15 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 1 | 37 | Note=Cytoplasmic;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=36;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 1 | 37 | Note=Cytoplasmic;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=16;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 1 | 37 | Note=Cytoplasmic;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=16;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 1 | 37 | Note=Cytoplasmic;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Substitution;Start=30;End=34 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 1 | 37 | Note=Cytoplasmic;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=35;End=404 |
| Q9NNX6 | Transmembrane | 38 | 58 | Note=Helical%3B Signal-anchor for type II membrane protein;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=36;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Transmembrane | 38 | 58 | Note=Helical%3B Signal-anchor for type II membrane protein;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=36;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Transmembrane | 38 | 58 | Note=Helical%3B Signal-anchor for type II membrane protein;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=36;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Transmembrane | 38 | 58 | Note=Helical%3B Signal-anchor for type II membrane protein;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=36;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Transmembrane | 38 | 58 | Note=Helical%3B Signal-anchor for type II membrane protein;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=16;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Transmembrane | 38 | 58 | Note=Helical%3B Signal-anchor for type II membrane protein;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=16;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Transmembrane | 38 | 58 | Note=Helical%3B Signal-anchor for type II membrane protein;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=35;End=404 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 59 | 404 | Note=Extracellular;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=36;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 59 | 404 | Note=Extracellular;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=36;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 59 | 404 | Note=Extracellular;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=191;End=236 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 59 | 404 | Note=Extracellular;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=36;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 59 | 404 | Note=Extracellular;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Substitution;Start=301;End=321 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 59 | 404 | Note=Extracellular;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=322;End=404 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 59 | 404 | Note=Extracellular;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=301;End=306 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 59 | 404 | Note=Extracellular;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=158;End=249 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 59 | 404 | Note=Extracellular;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=74;End=309 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 59 | 404 | Note=Extracellular;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=36;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 59 | 404 | Note=Extracellular;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=16;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 59 | 404 | Note=Extracellular;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=16;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 59 | 404 | Note=Extracellular;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=142;End=233 |
| Q9NNX6 | Topological domain | 59 | 404 | Note=Extracellular;Ontology_term=ECO:0000305;evidence=ECO:0000305 | Type=Deletion;Start=35;End=404 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 96 | 118 | Note=1 | Type=Deletion;Start=74;End=309 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 96 | 118 | Note=1 | Type=Deletion;Start=35;End=404 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 119 | 141 | Note=2 | Type=Deletion;Start=74;End=309 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 119 | 141 | Note=2 | Type=Deletion;Start=35;End=404 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 142 | 164 | Note=3 | Type=Deletion;Start=158;End=249 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 142 | 164 | Note=3 | Type=Deletion;Start=74;End=309 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 142 | 164 | Note=3 | Type=Deletion;Start=142;End=233 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 142 | 164 | Note=3 | Type=Deletion;Start=35;End=404 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 165 | 187 | Note=4 | Type=Deletion;Start=158;End=249 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 165 | 187 | Note=4 | Type=Deletion;Start=74;End=309 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 165 | 187 | Note=4 | Type=Deletion;Start=142;End=233 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 165 | 187 | Note=4 | Type=Deletion;Start=35;End=404 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 188 | 210 | Note=5 | Type=Deletion;Start=191;End=236 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 188 | 210 | Note=5 | Type=Deletion;Start=158;End=249 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 188 | 210 | Note=5 | Type=Deletion;Start=74;End=309 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 188 | 210 | Note=5 | Type=Deletion;Start=142;End=233 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 188 | 210 | Note=5 | Type=Deletion;Start=35;End=404 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 211 | 233 | Note=6 | Type=Deletion;Start=191;End=236 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 211 | 233 | Note=6 | Type=Deletion;Start=158;End=249 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 211 | 233 | Note=6 | Type=Deletion;Start=74;End=309 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 211 | 233 | Note=6 | Type=Deletion;Start=142;End=233 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 211 | 233 | Note=6 | Type=Deletion;Start=35;End=404 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 234 | 257 | Note=7 | Type=Deletion;Start=191;End=236 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 234 | 257 | Note=7 | Type=Deletion;Start=158;End=249 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 234 | 257 | Note=7 | Type=Deletion;Start=74;End=309 |
| Q9NNX6 | Repeat | 234 | 257 | Note=7 | Type=Deletion;Start=35;End=404 |
| Q9NNX6 | Domain | 263 | 378 | Note=C-type lectin;Ontology_term=ECO:0000255;evidence=ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00040 | Type=Substitution;Start=301;End=321 |
| Q9NNX6 | Domain | 263 | 378 | Note=C-type lectin;Ontology_term=ECO:0000255;evidence=ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00040 | Type=Deletion;Start=322;End=404 |
| Q9NNX6 | Domain | 263 | 378 | Note=C-type lectin;Ontology_term=ECO:0000255;evidence=ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00040 | Type=Deletion;Start=301;End=306 |
| Q9NNX6 | Domain | 263 | 378 | Note=C-type lectin;Ontology_term=ECO:0000255;evidence=ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00040 | Type=Deletion;Start=74;End=309 |
| Q9NNX6 | Domain | 263 | 378 | Note=C-type lectin;Ontology_term=ECO:0000255;evidence=ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00040 | Type=Deletion;Start=35;End=404 |
| Q9NNX6 | Region | 96 | 257 | Note=7 X approximate tandem repeats | Type=Deletion;Start=191;End=236 |
| Q9NNX6 | Region | 96 | 257 | Note=7 X approximate tandem repeats | Type=Deletion;Start=158;End=249 |
| Q9NNX6 | Region | 96 | 257 | Note=7 X approximate tandem repeats | Type=Deletion;Start=74;End=309 |
| Q9NNX6 | Region | 96 | 257 | Note=7 X approximate tandem repeats | Type=Deletion;Start=142;End=233 |
| Q9NNX6 | Region | 96 | 257 | Note=7 X approximate tandem repeats | Type=Deletion;Start=35;End=404 |
| Q9NNX6 | Motif | 14 | 15 | Note=Endocytosis signal | Type=Substitution;Start=1;End=15 |
| Q9NNX6 | Motif | 14 | 15 | Note=Endocytosis signal | Type=Substitution;Start=1;End=15 |
| Q9NNX6 | Motif | 14 | 15 | Note=Endocytosis signal | Type=Substitution;Start=1;End=15 |
| Q9NNX6 | Motif | 14 | 15 | Note=Endocytosis signal | Type=Substitution;Start=1;End=15 |
| Q9NNX6 | Motif | 16 | 18 | Note=Endocytosis signal;Ontology_term=ECO:0000255;evidence=ECO:0000255 | Type=Deletion;Start=16;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Motif | 16 | 18 | Note=Endocytosis signal;Ontology_term=ECO:0000255;evidence=ECO:0000255 | Type=Deletion;Start=16;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Motif | 31 | 34 | Note=Endocytosis signal;Ontology_term=ECO:0000255;evidence=ECO:0000255 | Type=Deletion;Start=16;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Motif | 31 | 34 | Note=Endocytosis signal;Ontology_term=ECO:0000255;evidence=ECO:0000255 | Type=Deletion;Start=16;End=59 |
| Q9NNX6 | Motif | 31 | 34 | Note=Endocytosis signal;Ontology_term=ECO:0000255;evidence=ECO:0000255 | Type=Substitution;Start=30;End=34 |
Gene Isoform Structures and Expression Levels for CD209 |
 Gene structures of our canonical and alternative spliced genes of CD209 Gene structures of our canonical and alternative spliced genes of CD209* Click on the image to open the UCSC genome browser with custom track showing this image in a new window. |
 Expression levels of gene isoforms across GTEx. Expression levels of gene isoforms across GTEx. |
 Expression levels of gene isoforms across TCGA. Expression levels of gene isoforms across TCGA. |
Protein Structures |
 PDB and CIF files of the predicted protein structures PDB and CIF files of the predicted protein structures * Here we show the 3D structure of the proteins using Mol*. AlphaFold produces a per-residue confidence score (pLDDT) between 0 and 100. Model confidence is shown from the pLDDT values per residue. pLDDT corresponds to the model’s prediction of its score on the local Distance Difference Test. It is a measure of local accuracy (from AlphfaFold website). To color code individual residues, we transformed individual PDB files into CIF format. |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1 |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-10 |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-11 |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-12 |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-2 |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-3 |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-4 |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-5 |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-6 |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-7 |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-8 |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-9 |
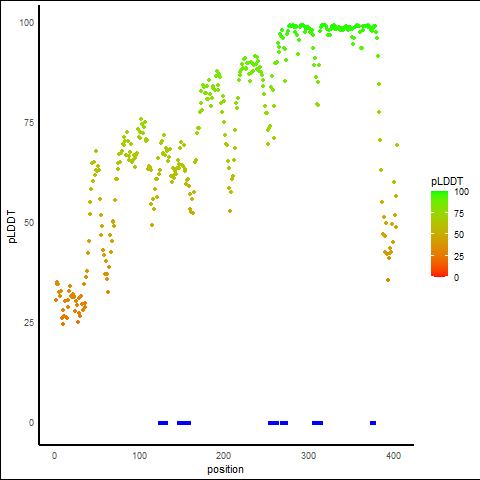
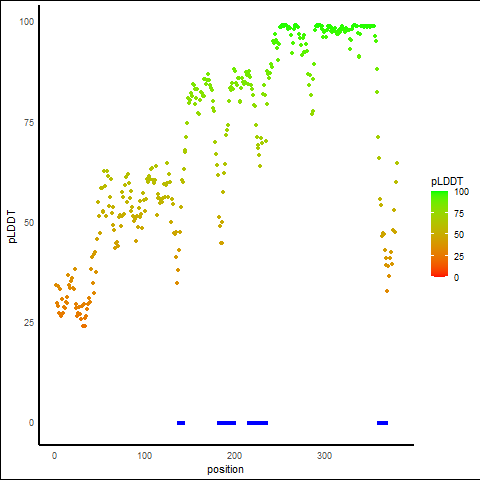
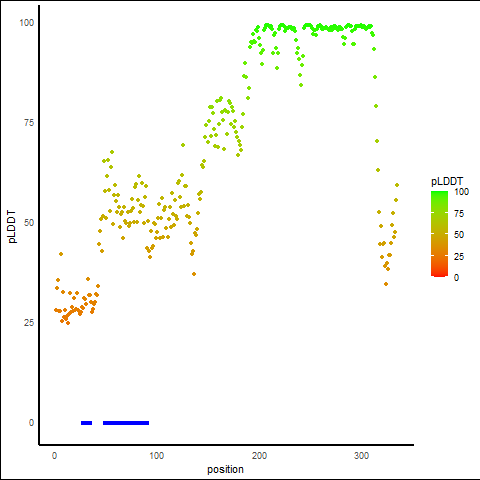
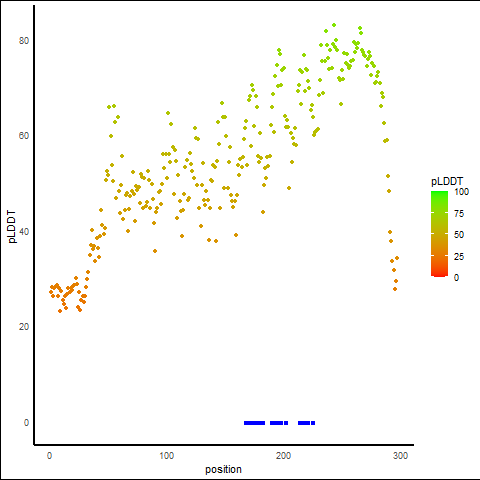
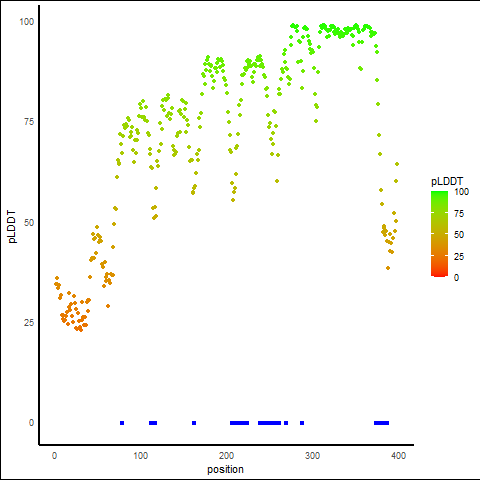
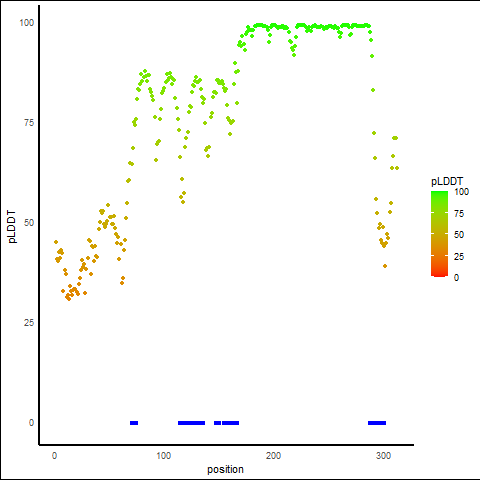
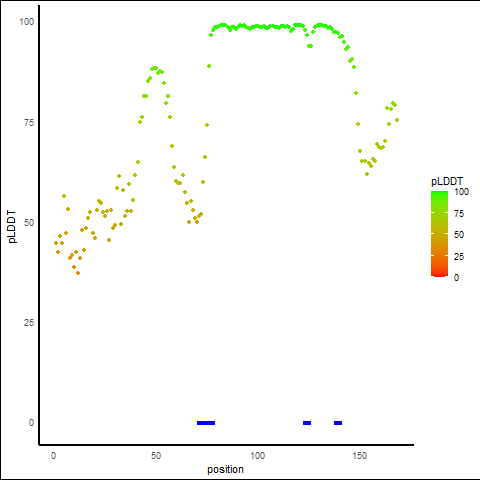
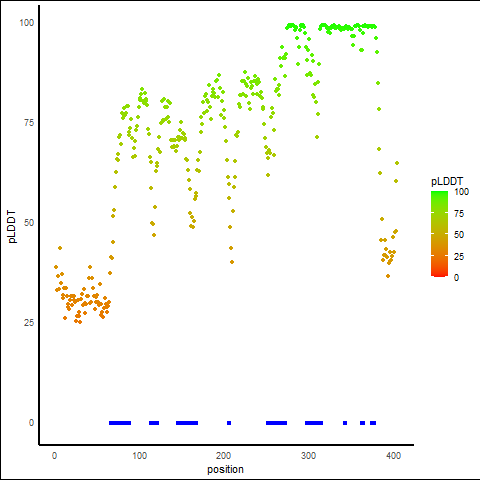
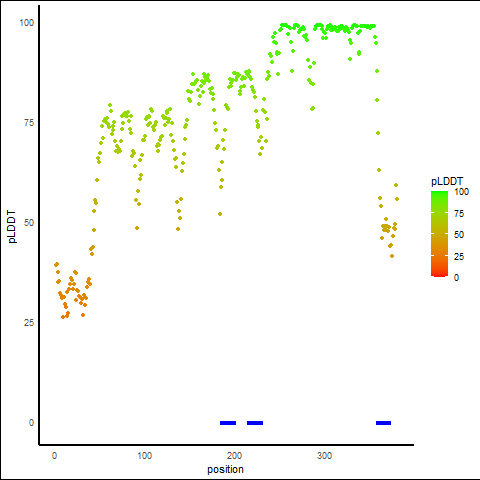
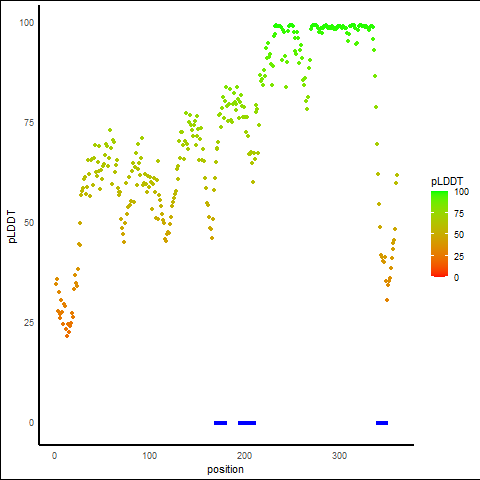
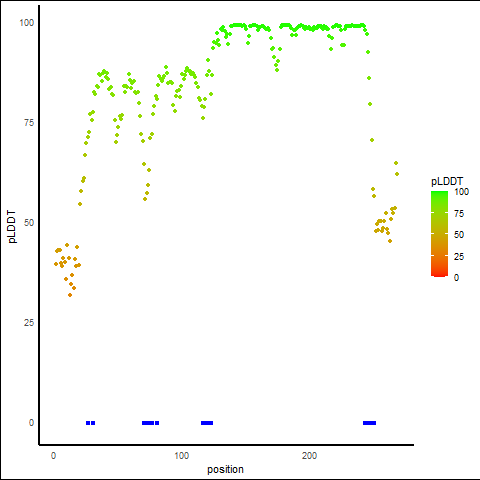
pLDDT Score Distribution |
 pLDDT score distribution of the predicted protein structures from AlphaFold2 pLDDT score distribution of the predicted protein structures from AlphaFold2* AlphaFold produces a per-residue confidence score (pLDDT) between 0 and 100. |
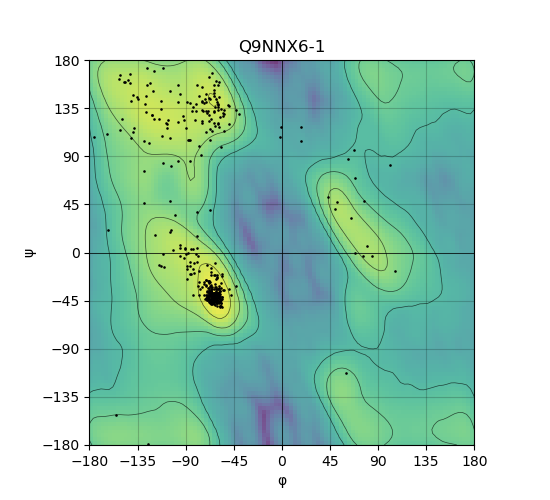
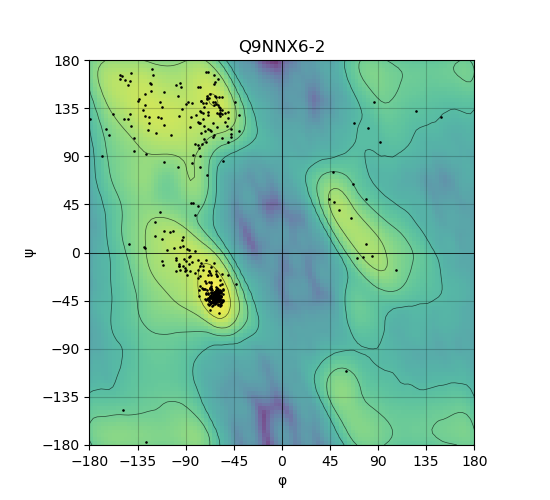
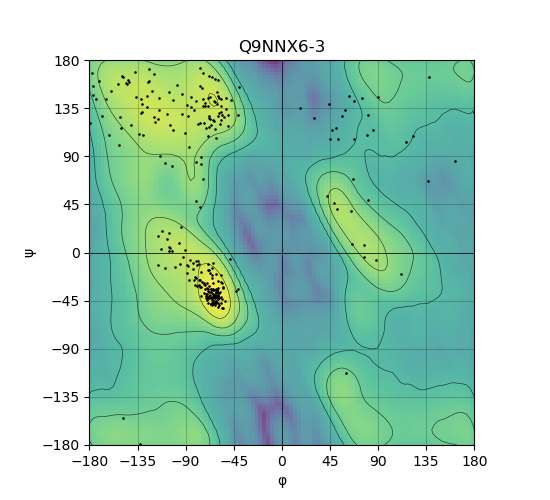
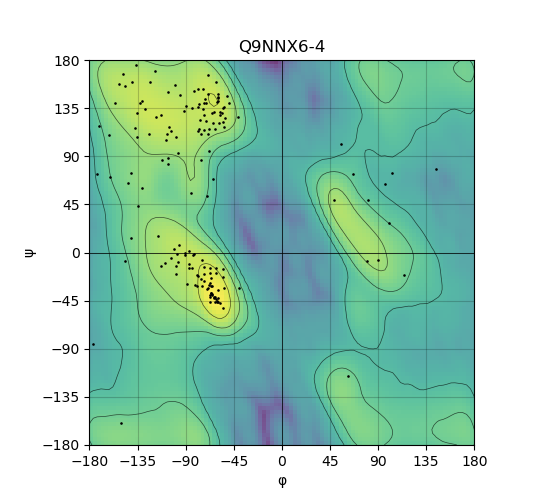
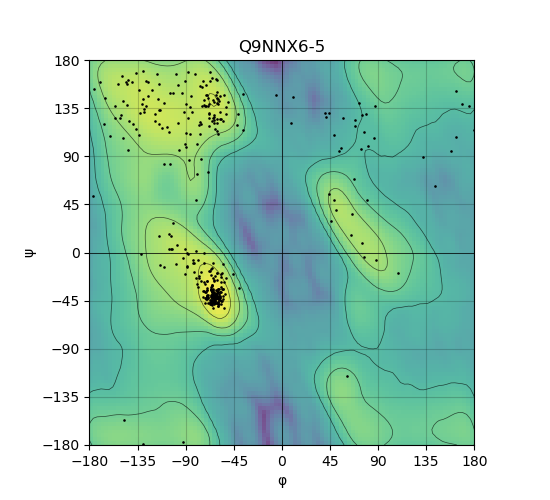
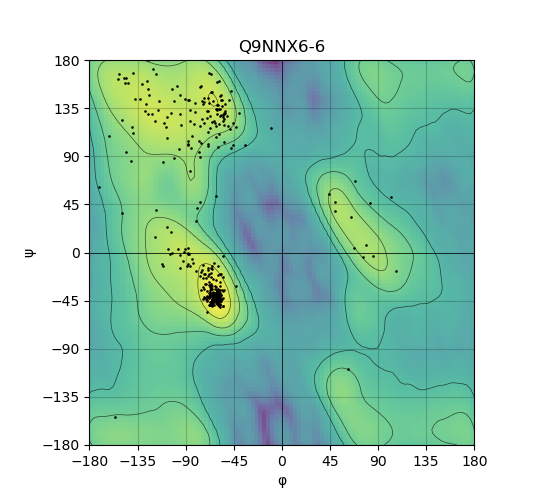
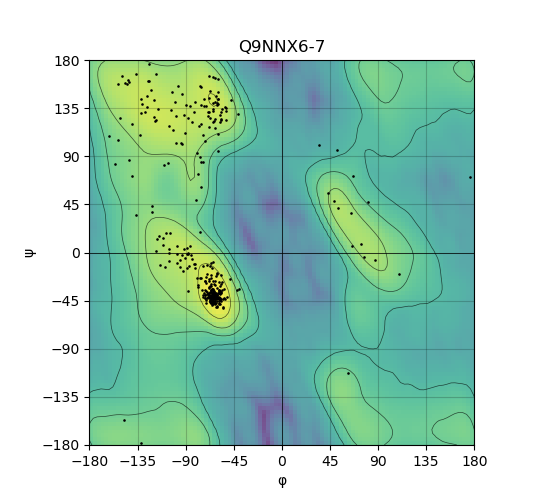
Ramachandran Plot of Protein Structures |
 Ramachandran plot of the torsional angles - phi (φ)and psi (ψ) - of the residues (amino acids) contained in this protein peptide. Ramachandran plot of the torsional angles - phi (φ)and psi (ψ) - of the residues (amino acids) contained in this protein peptide. |
Potential Active Site Information |
 The potential binding sites of these proteins were identified using SiteMap, a module of the Schrodinger suite. The potential binding sites of these proteins were identified using SiteMap, a module of the Schrodinger suite. |
| UniProt-id | Site score | Size | D score | Volume | Exposure | Enclosure | Contact | Phobic | Philic | Balance | Don/Acc | Residues |
| Q9NNX6-1 | 1.027 | 101 | 1.069 | 362.894 | 0.724 | 0.69 | 0.807 | 0.507 | 0.874 | 0.58 | 0.656 | 124,127,128,131,147,150,151,154,155,158,254,255,25 6,257,258,259,260,261,262,268,269,270,271,272,273, 306,307,310,312,314,374,375,376 |
| Q9NNX6-10 | 1.026 | 246 | 1.068 | 618.429 | 0.539 | 0.689 | 0.936 | 0.861 | 0.874 | 0.985 | 0.795 | 138,140,141,142,182,183,184,185,186,188,189,192,19 3,195,196,199,215,218,219,222,223,226,228,229,230, 232,233,234,360,361,362,363,364,367,368 |
| Q9NNX6-11 | 1.019 | 154 | 1.054 | 458.591 | 0.557 | 0.694 | 0.906 | 0.757 | 0.929 | 0.814 | 0.92 | 28,29,31,32,33,34,49,52,53,56,59,60,62,63,66,67,68 ,69,72,75,76,78,79,82,83,86,89,90 |
| Q9NNX6-12 | 1.147 | 94 | 1.252 | 198.254 | 0.495 | 0.746 | 0.995 | 2.672 | 0.327 | 8.164 | 1.409 | 168,169,172,174,175,176,178,179,182,190,191,194,19 5,198,202,214,217,218,220,221,225 |
| Q9NNX6-2 | 1.026 | 218 | 1.057 | 620.144 | 0.578 | 0.71 | 0.957 | 0.653 | 0.948 | 0.689 | 1.172 | 78,112,113,114,115,116,162,206,207,208,209,212,213 ,216,219,220,223,239,242,243,246,250,252,253,254,2 55,256,257,258,259,260,269,287,373,374,375,376,377 ,378,379,380,381,382,385,386 |
| Q9NNX6-3 | 1.041 | 270 | 1.073 | 527.877 | 0.448 | 0.727 | 0.993 | 0.82 | 0.93 | 0.882 | 0.728 | 70,74,114,115,116,117,120,121,124,125,127,128,131, 132,135,147,150,154,158,160,161,162,163,164,165,16 6,287,288,289,290,291,292,293,294,295,296,299,300 |
| Q9NNX6-4 | 0.885 | 79 | 0.881 | 188.307 | 0.503 | 0.647 | 0.974 | 0.447 | 1.052 | 0.425 | 0.786 | 71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,123,124,125,138,140
|
| Q9NNX6-5 | 1.041 | 423 | 1.083 | 1329.125 | 0.596 | 0.707 | 0.898 | 0.757 | 0.862 | 0.878 | 1.016 | 66,67,69,70,71,73,74,76,77,80,83,84,87,114,115,116 ,117,120,145,146,148,149,151,152,154,155,156,158,1 59,160,161,162,163,164,165,166,206,251,252,253,254 ,255,256,257,258,259,260,261,262,263,264,268,269,2 70,271,272,298,300,301,302,304,305,306,307,308,309 ,310,312,314,342,362,363,374,375,376 |
| Q9NNX6-6 | 1.016 | 182 | 1.059 | 371.126 | 0.516 | 0.673 | 0.919 | 0.803 | 0.872 | 0.921 | 1.221 | 185,186,188,189,192,193,195,199,215,218,219,222,22 6,227,229,359,360,361,362,363,364,365,367,368,369, 370,371 |
| Q9NNX6-7 | 1.056 | 114 | 1.085 | 288.806 | 0.535 | 0.755 | 1.096 | 1.04 | 0.945 | 1.101 | 0.959 | 169,172,173,175,176,179,195,198,199,202,206,209,34 0,341,342,343,344,347,348 |
| Q9NNX6-8 | 1.051 | 107 | 1.077 | 190.365 | 0.409 | 0.753 | 1.075 | 1.133 | 0.966 | 1.173 | 1.067 | 26,30,70,71,72,73,76,80,116,117,118,119,120,121,12 2,243,244,245,246,247,248,250 |
Protein Structure and Feature Comparision |
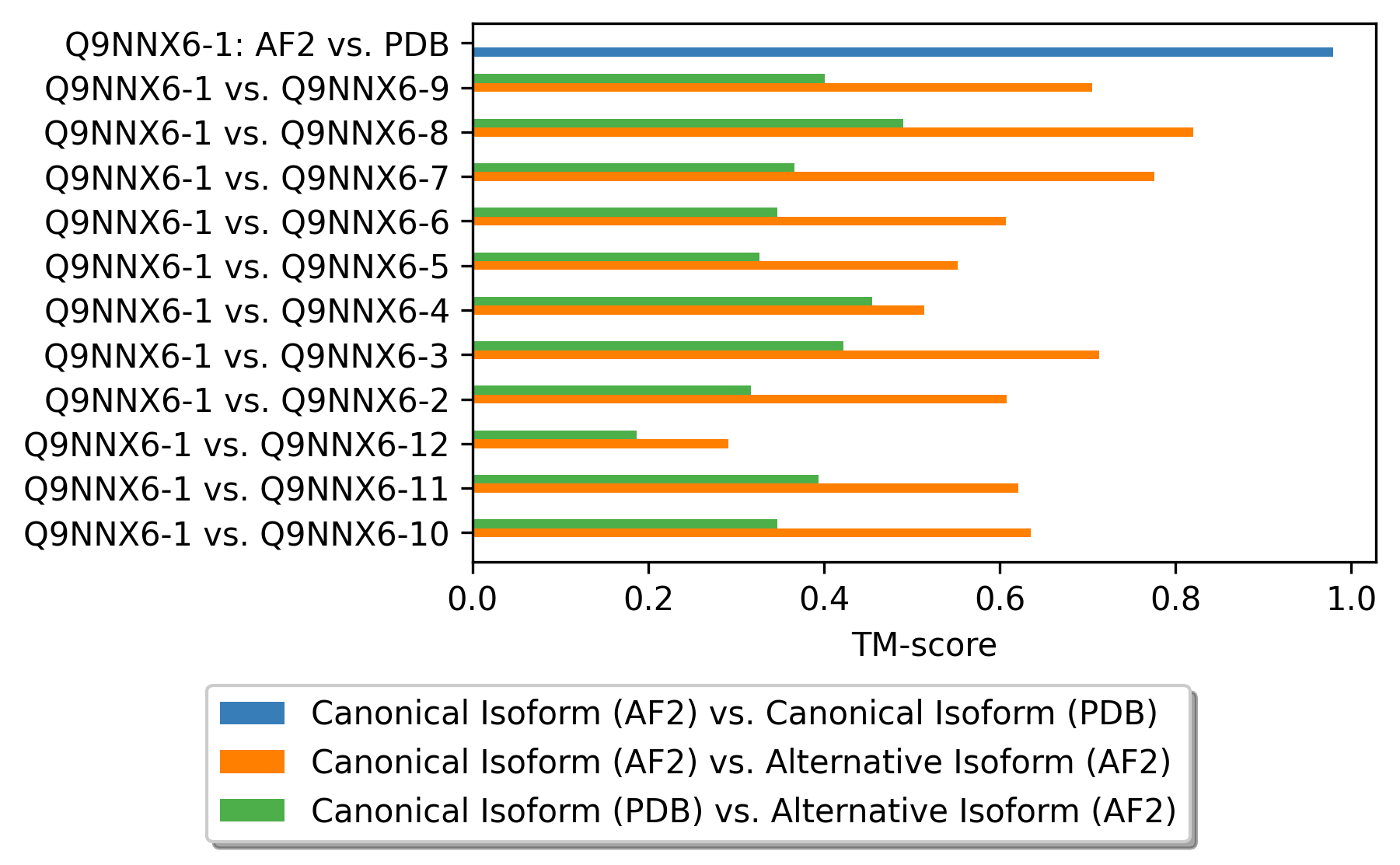
 Protein Structure Comparision Using Template Modeling Scores (TM-score). Protein Structure Comparision Using Template Modeling Scores (TM-score). |
 |
 Protein Structure Comparision Visualization with mol*. between Canonical predicted structure (AF2)(orange) vs Canonical validated structure (PDB)(green) Protein Structure Comparision Visualization with mol*. between Canonical predicted structure (AF2)(orange) vs Canonical validated structure (PDB)(green) |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_Q9NNX6-1_6ghv_C.pdb |
 Protein Structure Comparision Visualization with mol*. between Canonical validated structure (PDB)(orange) vs Alternative predicted structure (AF2)(green) Protein Structure Comparision Visualization with mol*. between Canonical validated structure (PDB)(orange) vs Alternative predicted structure (AF2)(green) |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_6ghv_C_Q9NNX6-10.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_6ghv_C_Q9NNX6-11.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_6ghv_C_Q9NNX6-12.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_6ghv_C_Q9NNX6-2.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_6ghv_C_Q9NNX6-3.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_6ghv_C_Q9NNX6-4.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_6ghv_C_Q9NNX6-5.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_6ghv_C_Q9NNX6-6.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_6ghv_C_Q9NNX6-7.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_6ghv_C_Q9NNX6-8.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_6ghv_C_Q9NNX6-9.pdb |
 Protein Structure Comparision Visualization with mol*. between Canonical predicted structure (AF2)(orange) vs Alternative predicted structure (AF2)(green) Protein Structure Comparision Visualization with mol*. between Canonical predicted structure (AF2)(orange) vs Alternative predicted structure (AF2)(green) |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_Q9NNX6-10.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_Q9NNX6-11.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_Q9NNX6-12.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_Q9NNX6-2.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_Q9NNX6-3.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_Q9NNX6-4.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_Q9NNX6-5.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_Q9NNX6-6.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_Q9NNX6-7.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_Q9NNX6-8.pdb |
| 3D view using mol* of Q9NNX6-1_Q9NNX6-9.pdb |
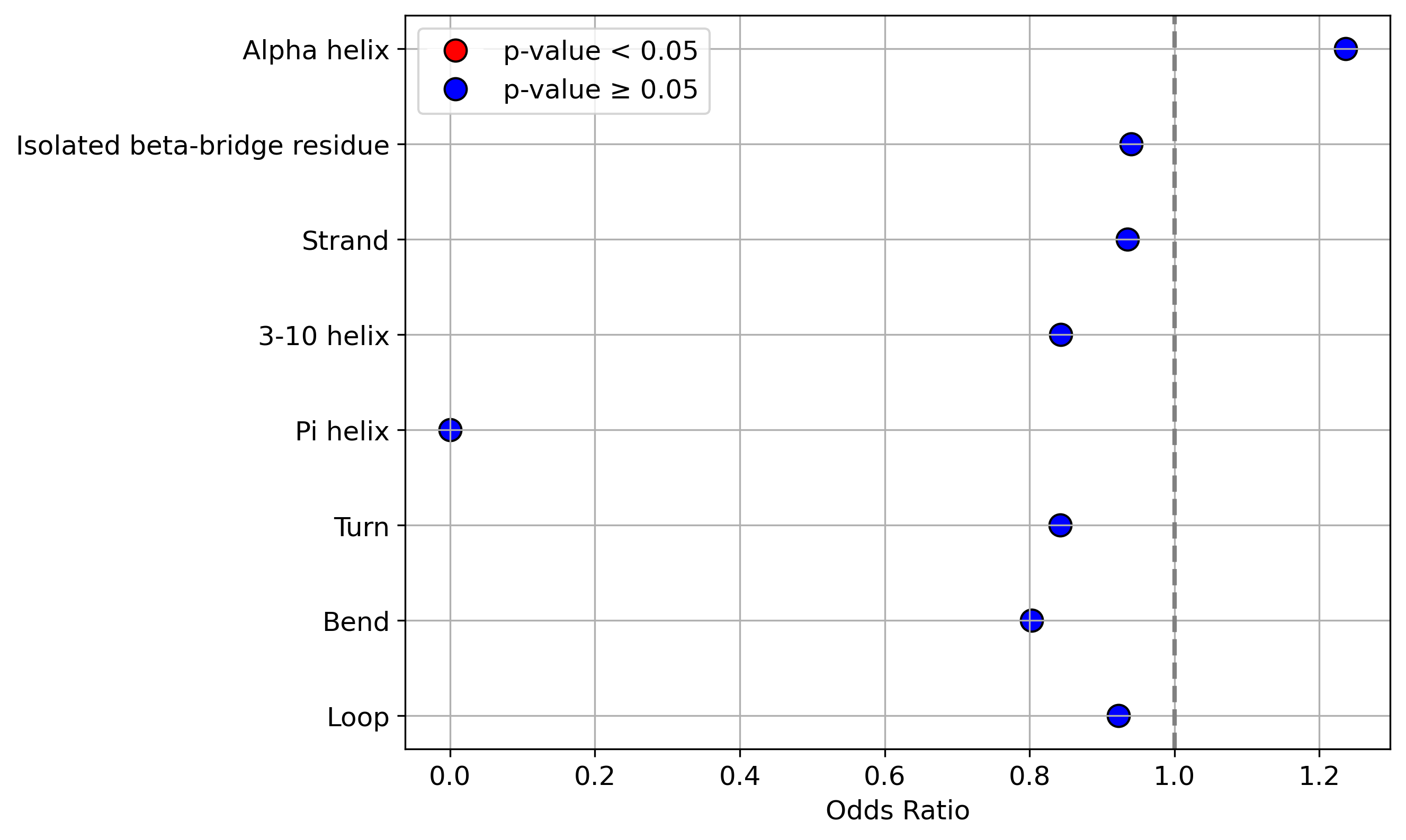
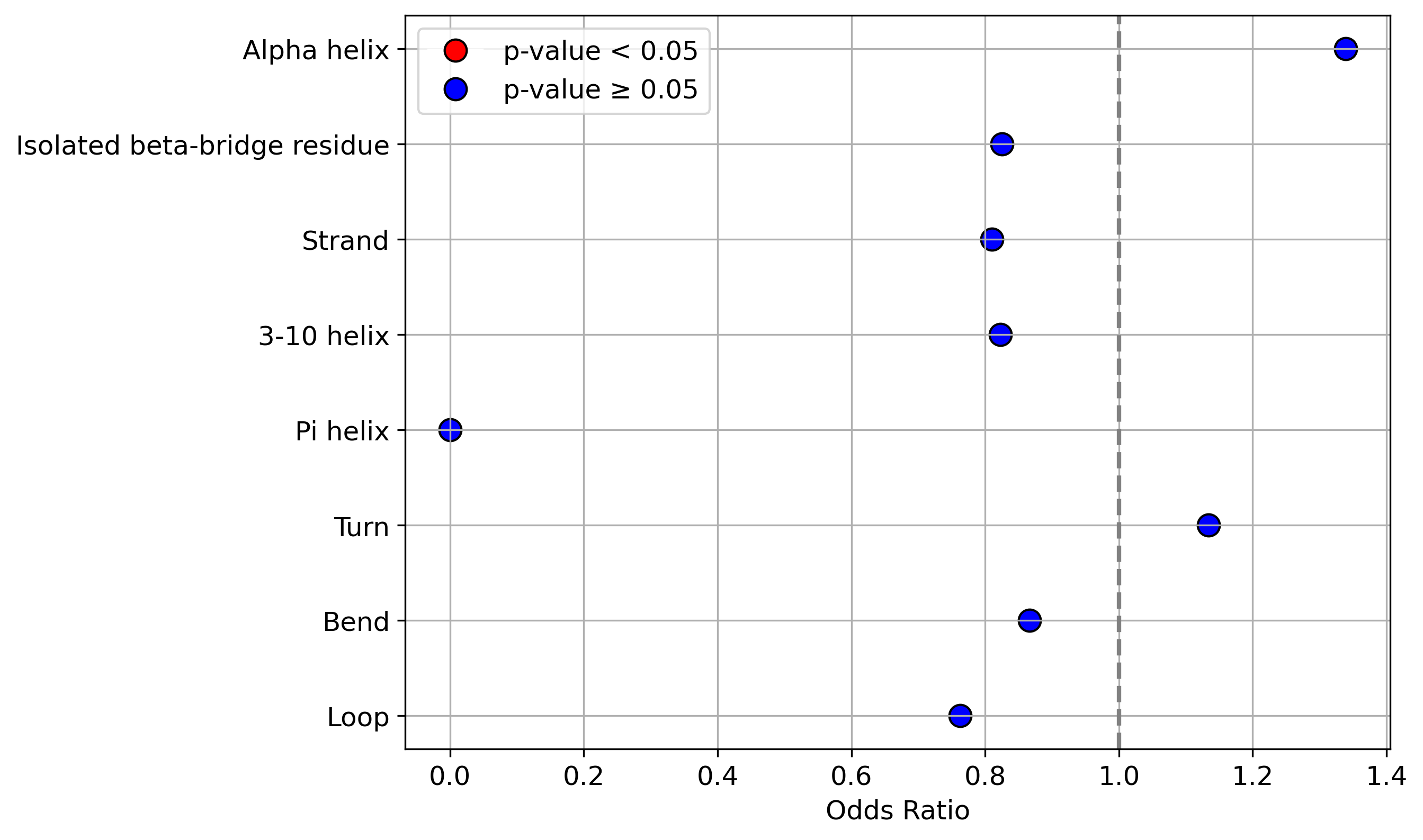
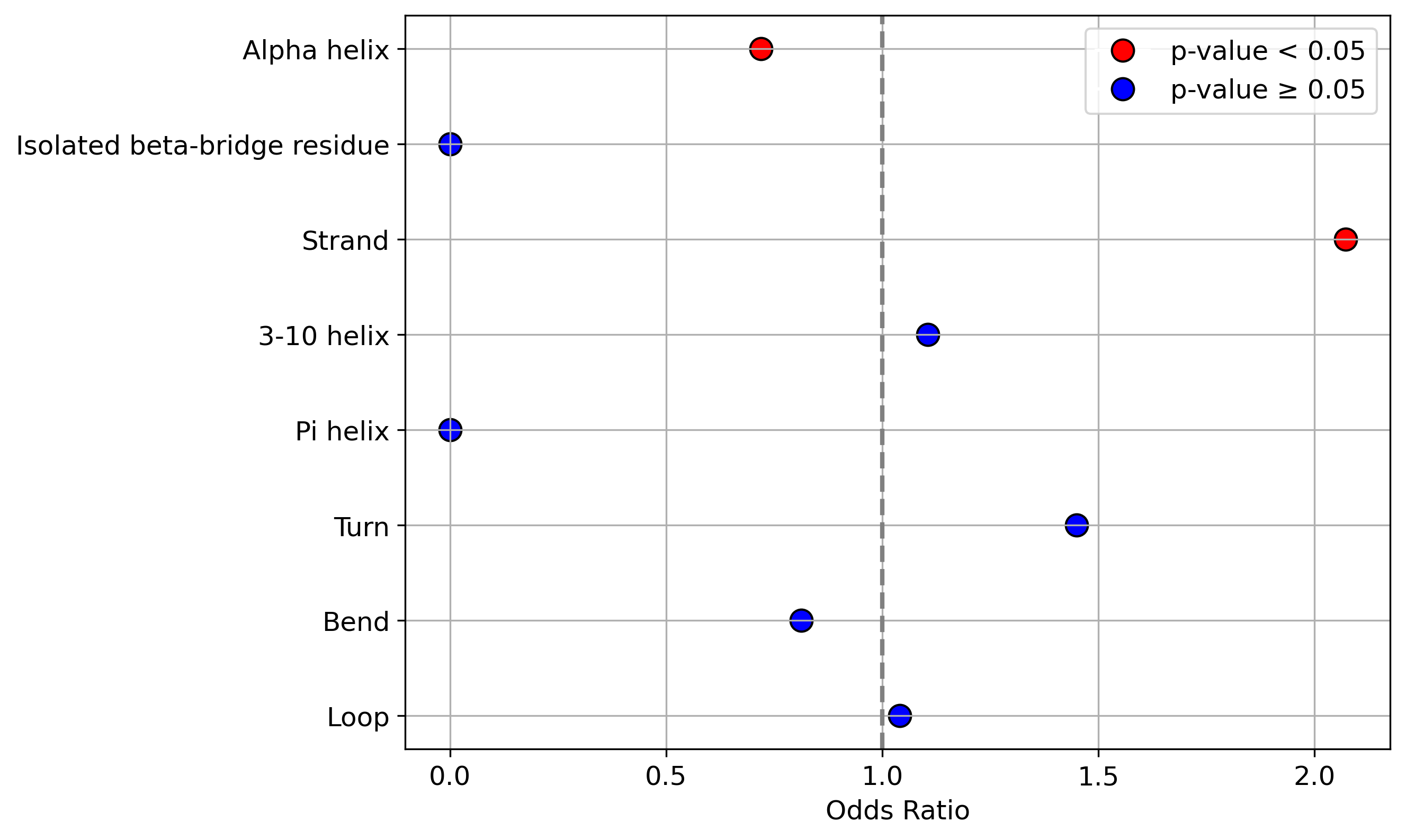
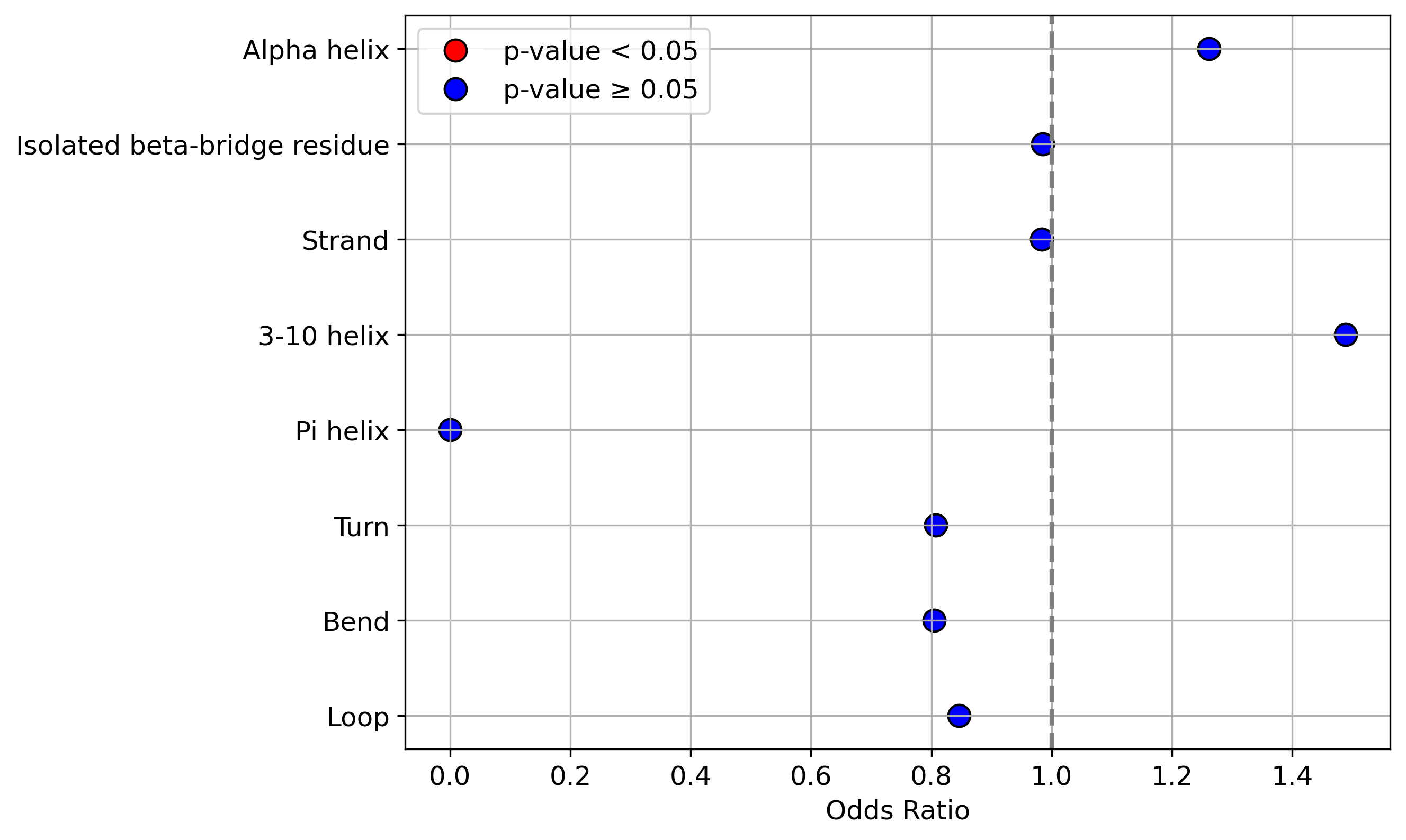
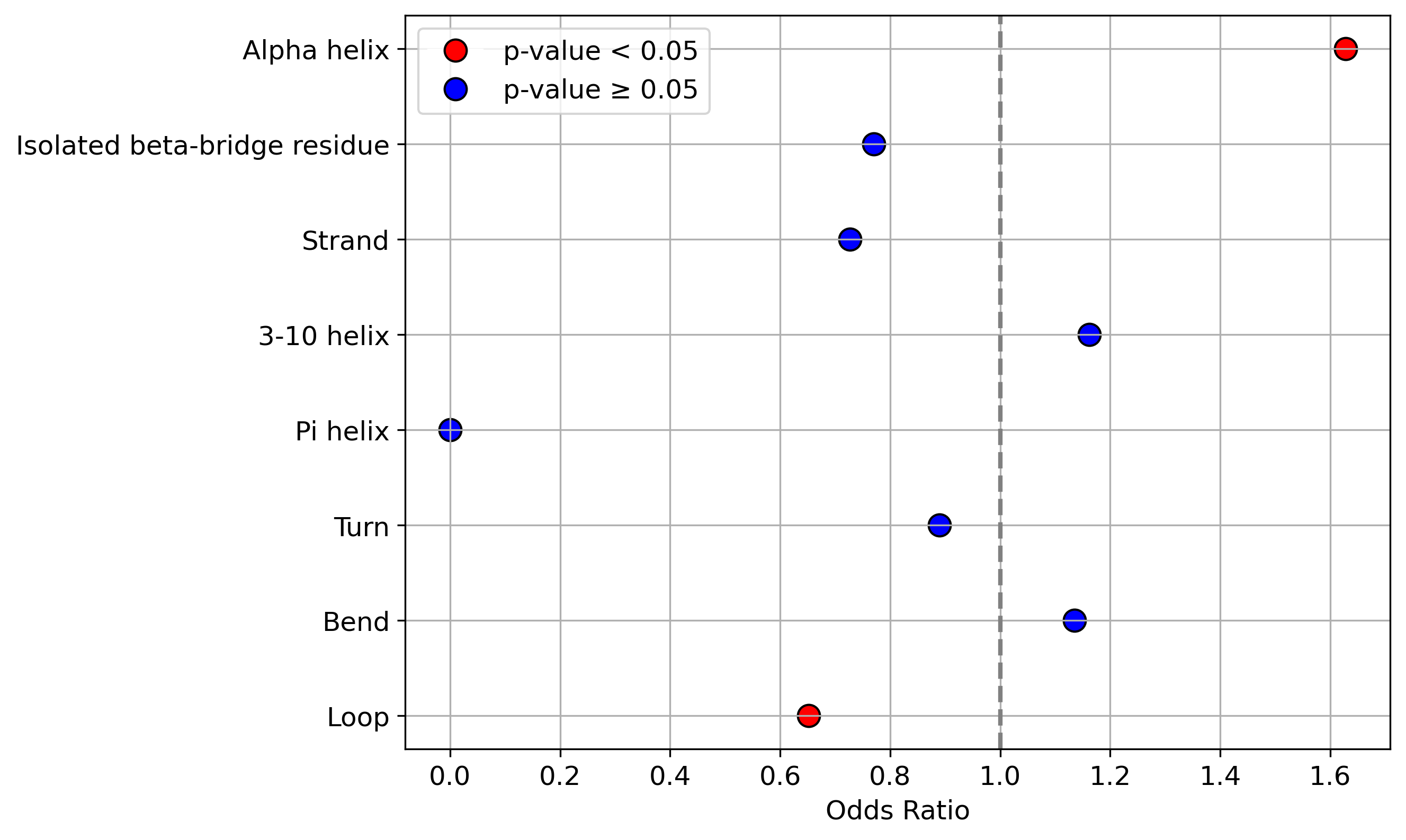
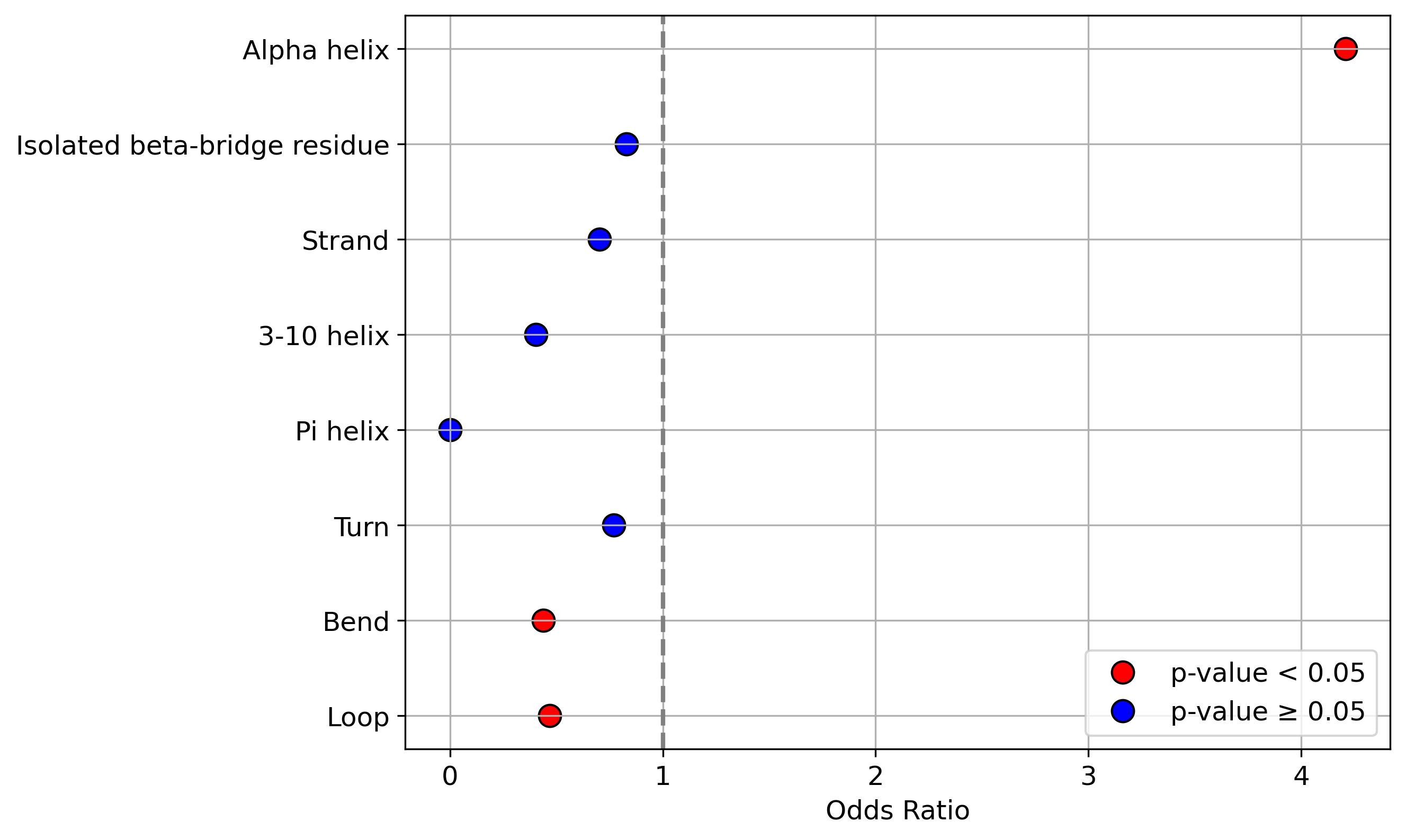
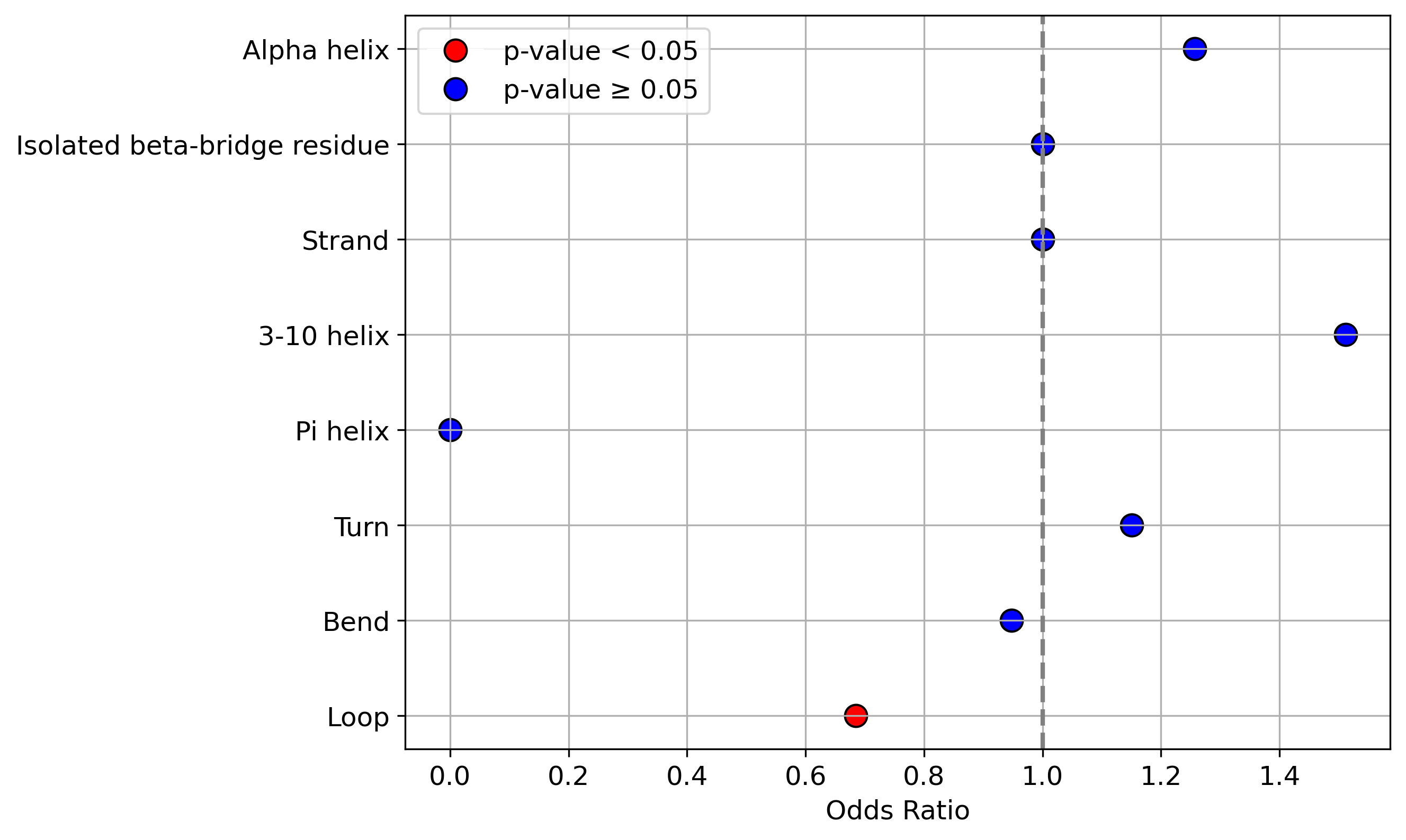
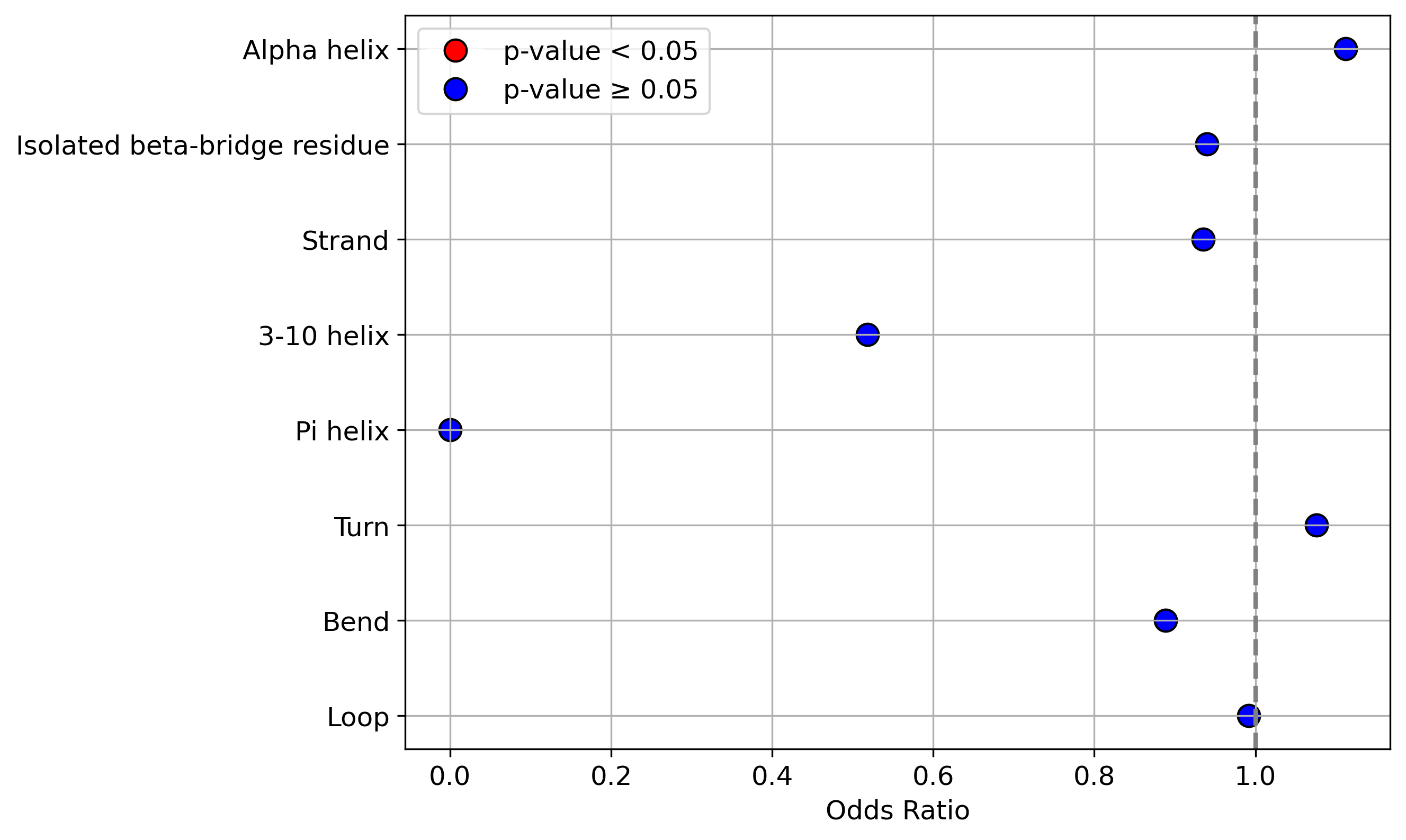
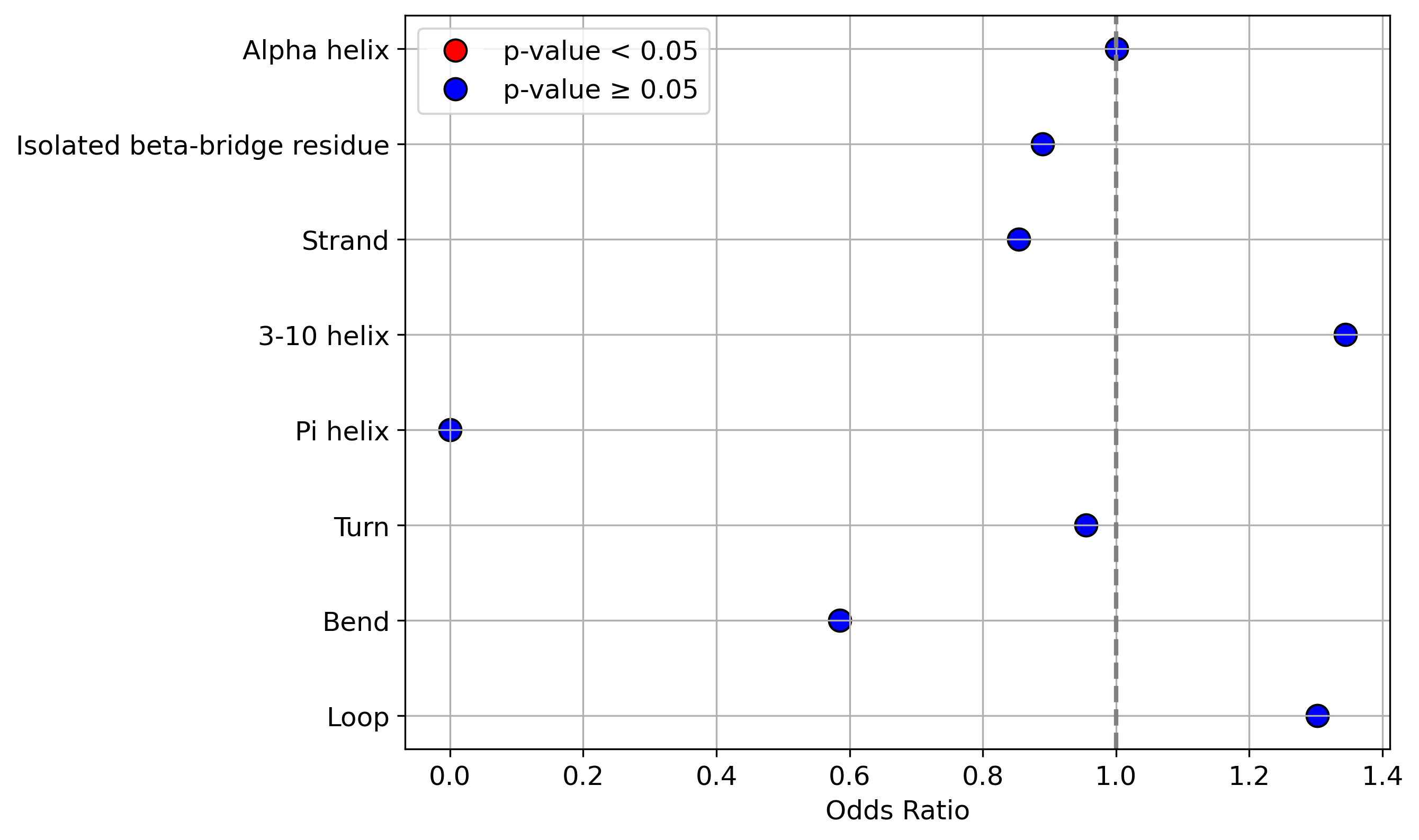
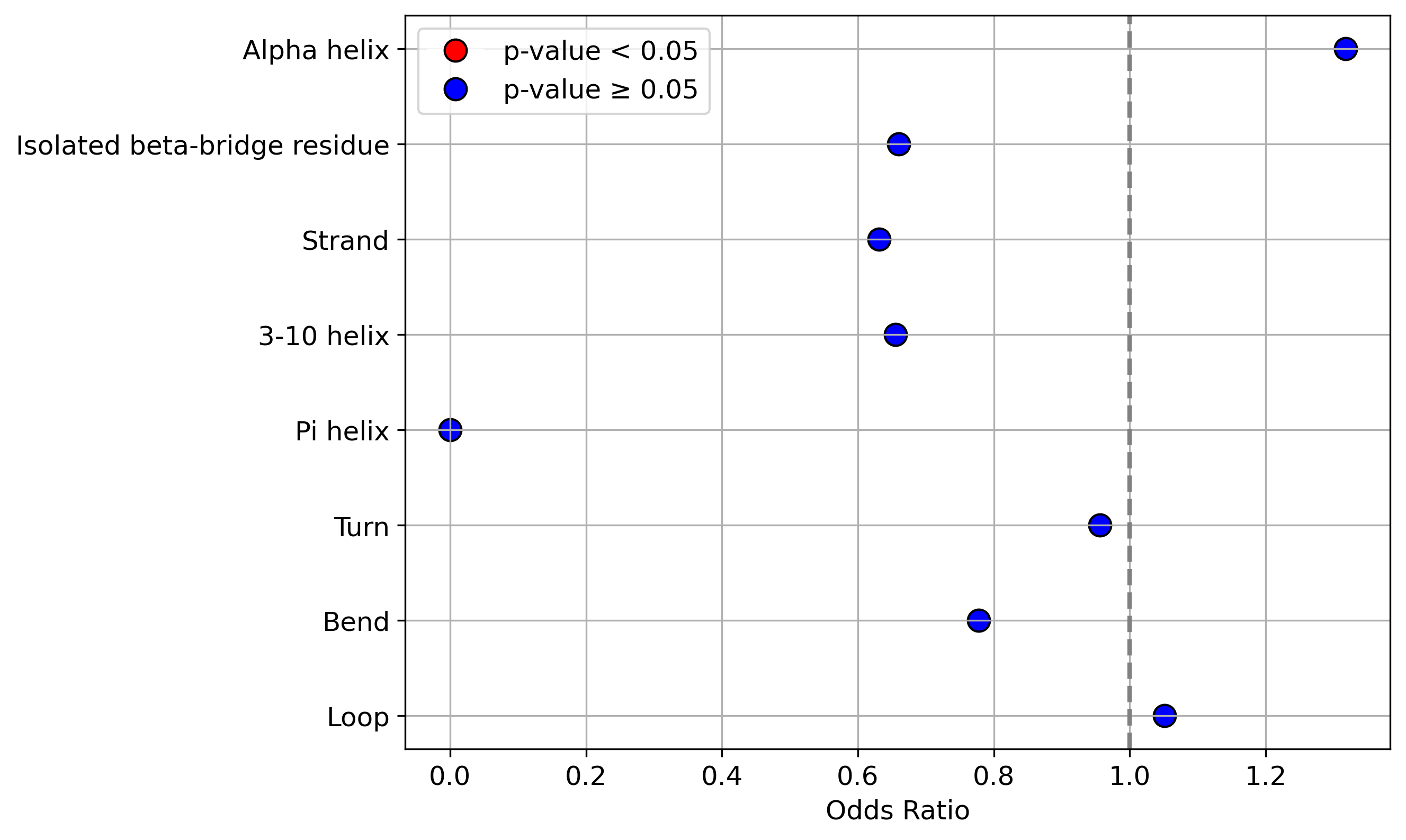
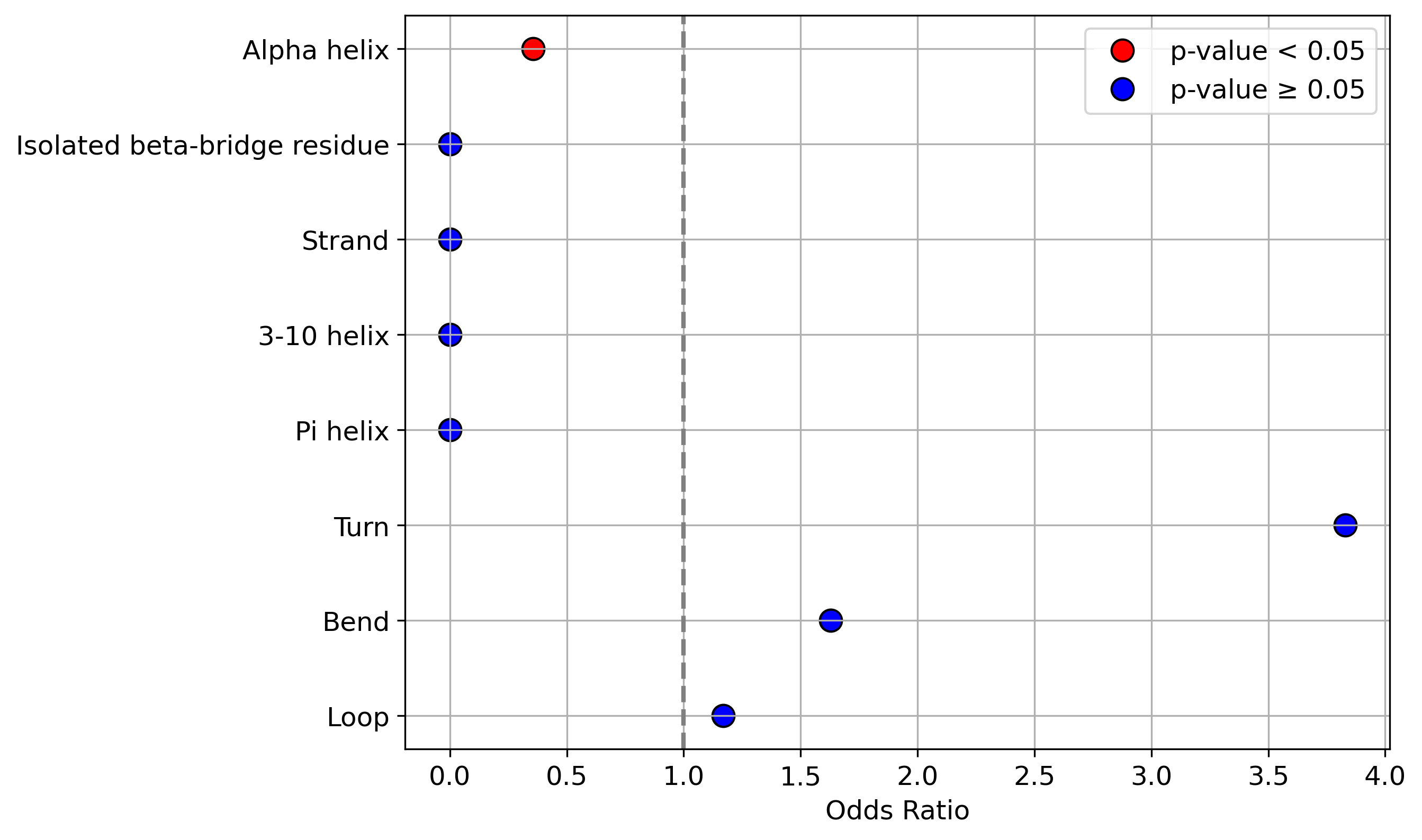
 Protein Feature Comparison of the protein sequendary structures among the protiens. Protein Feature Comparison of the protein sequendary structures among the protiens. |
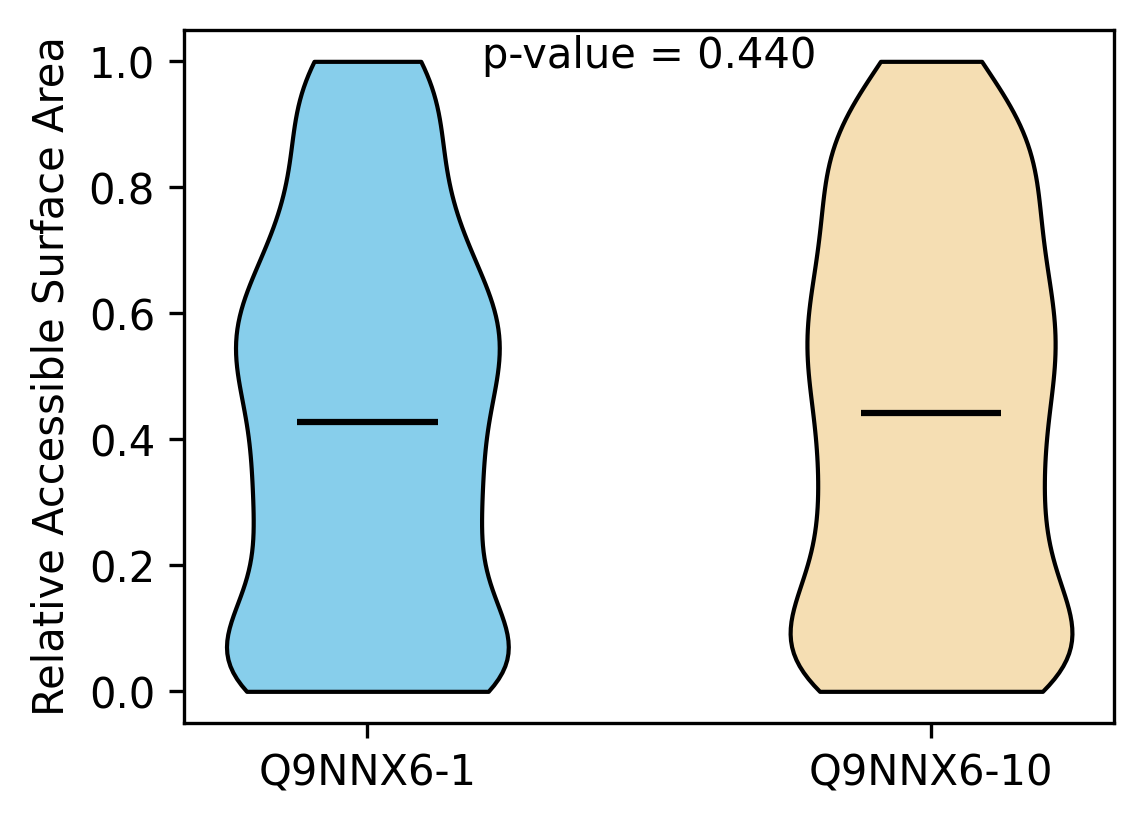
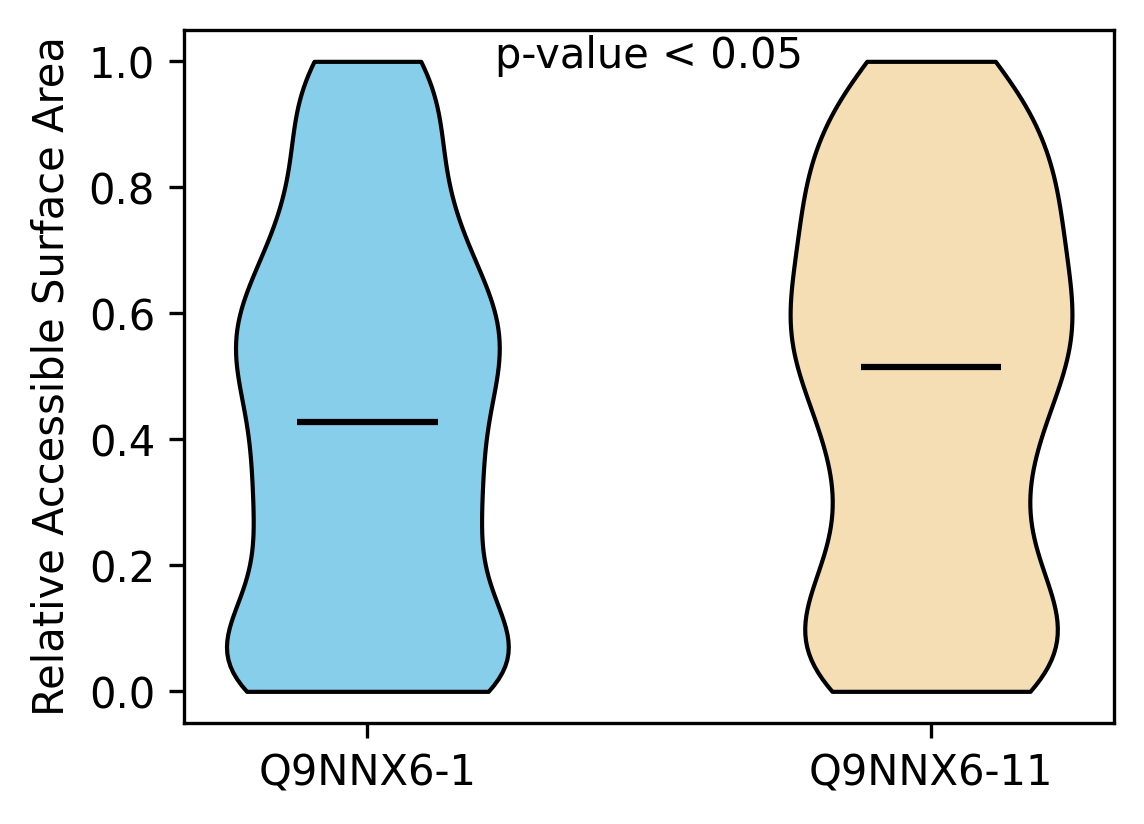
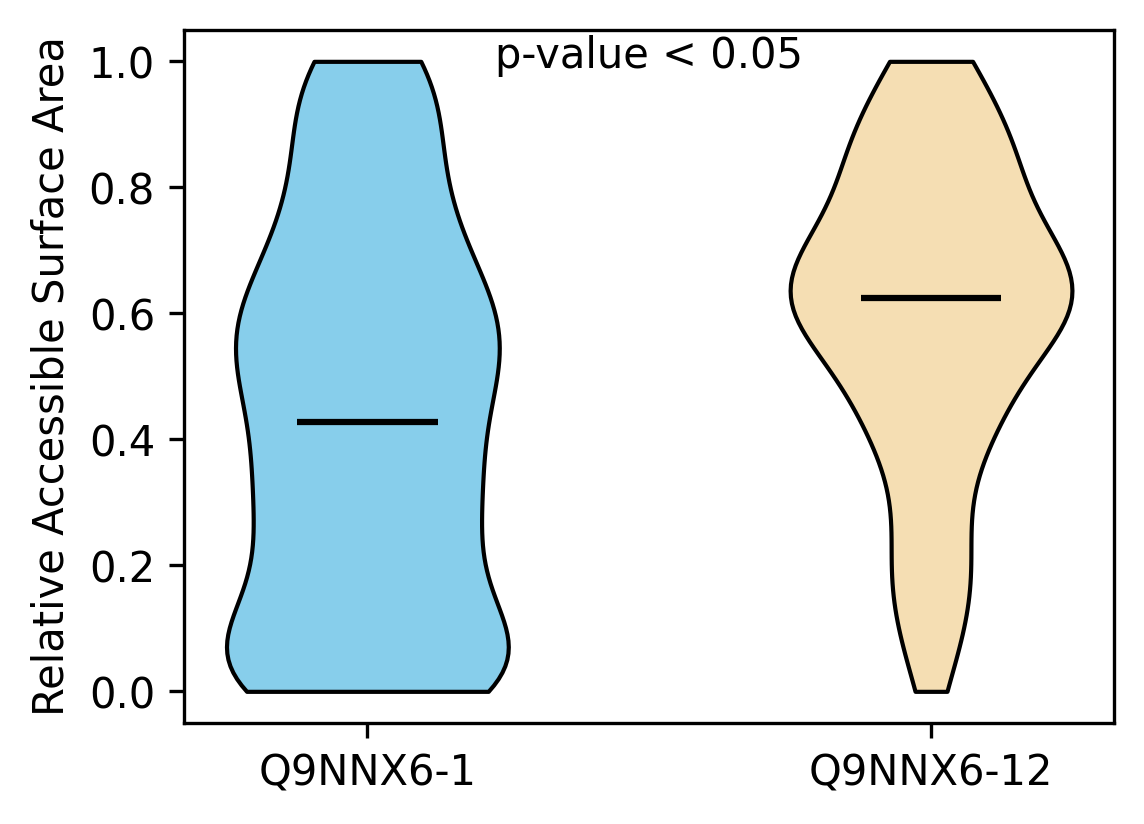
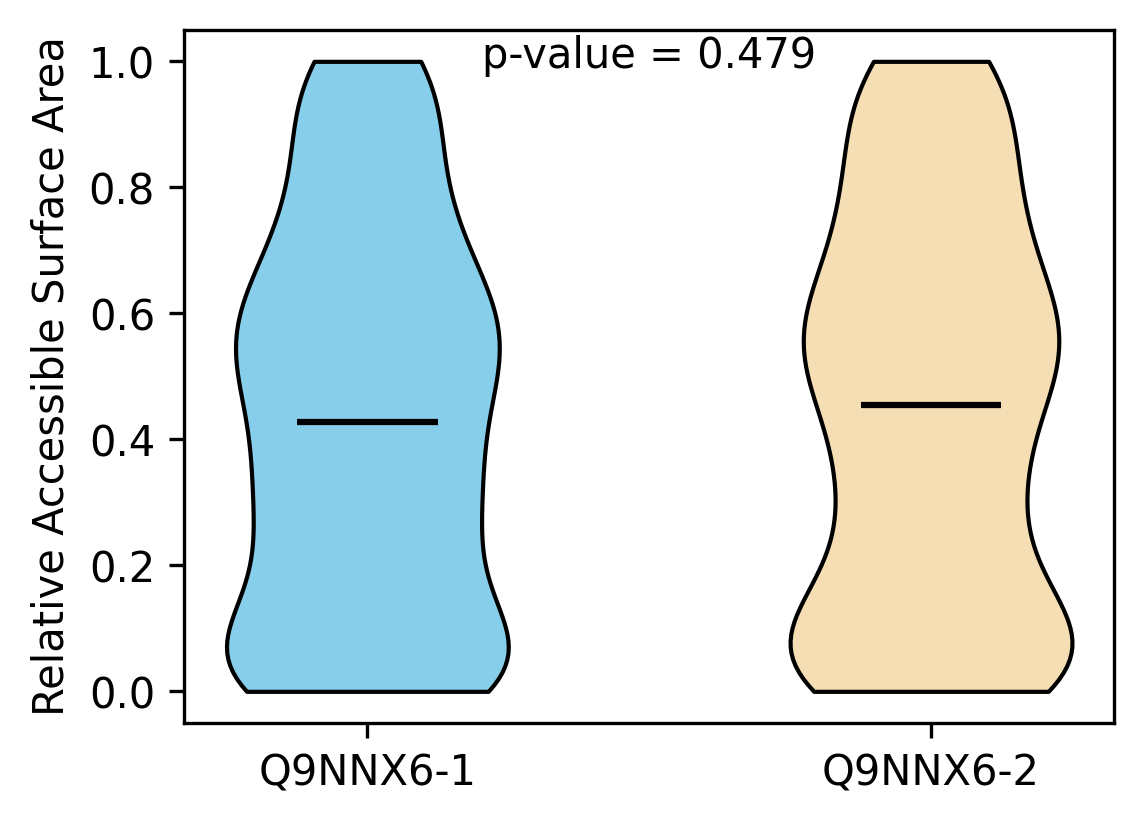
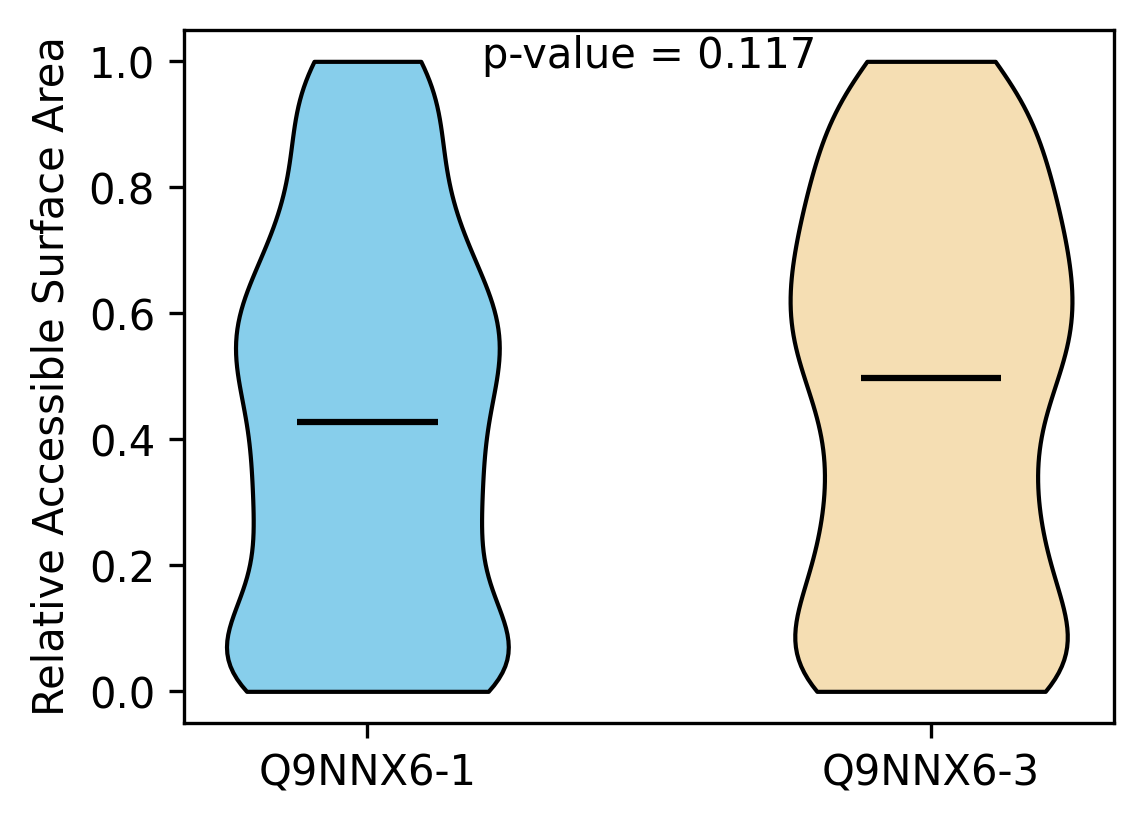
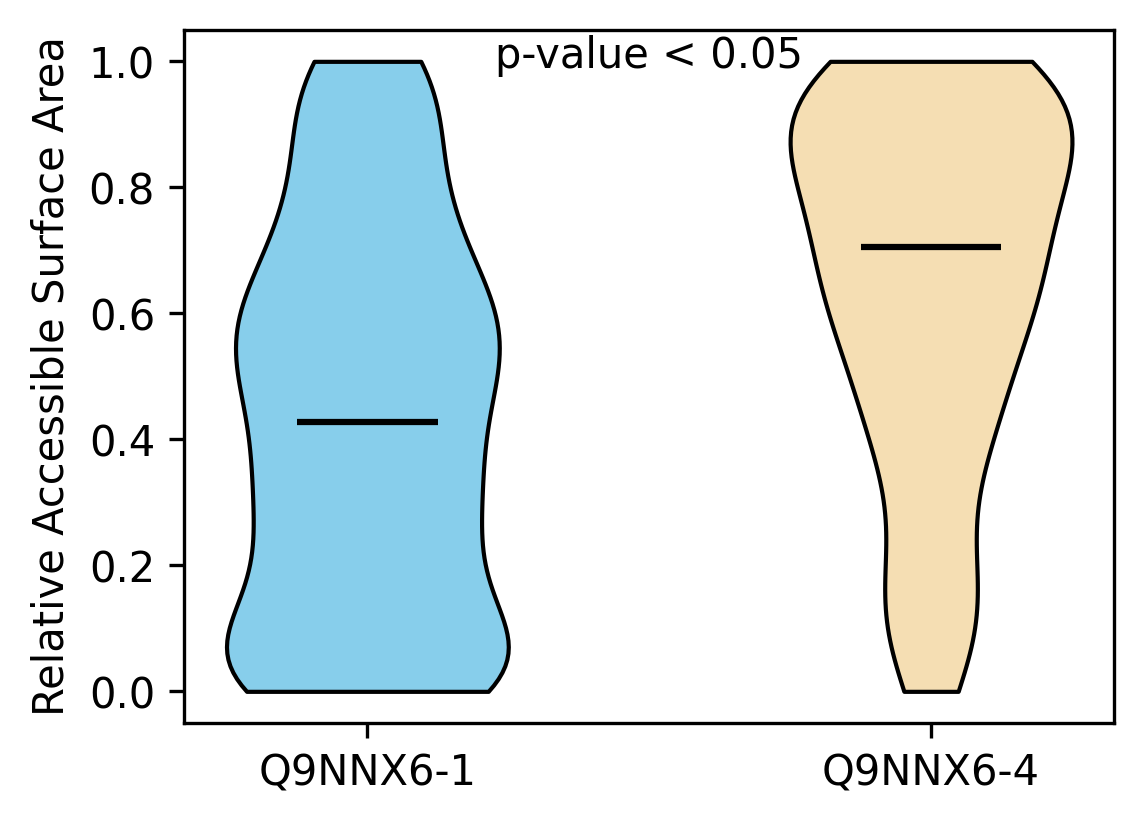
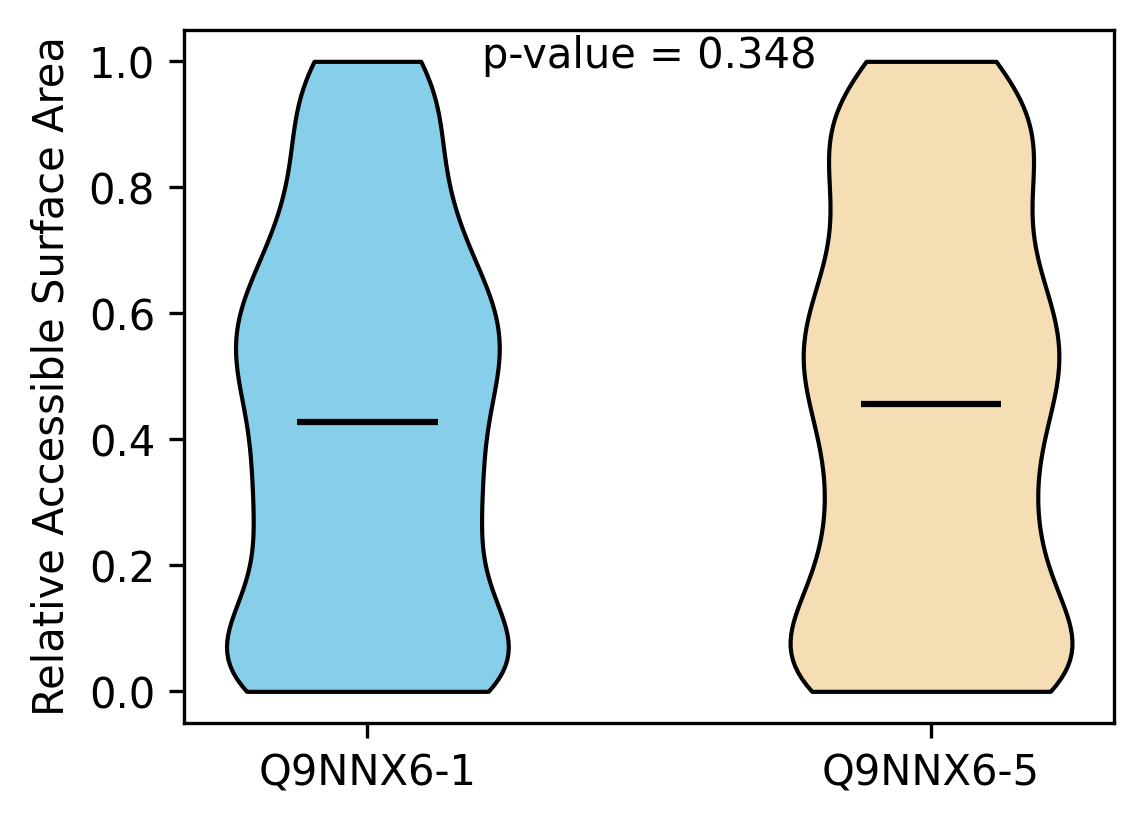
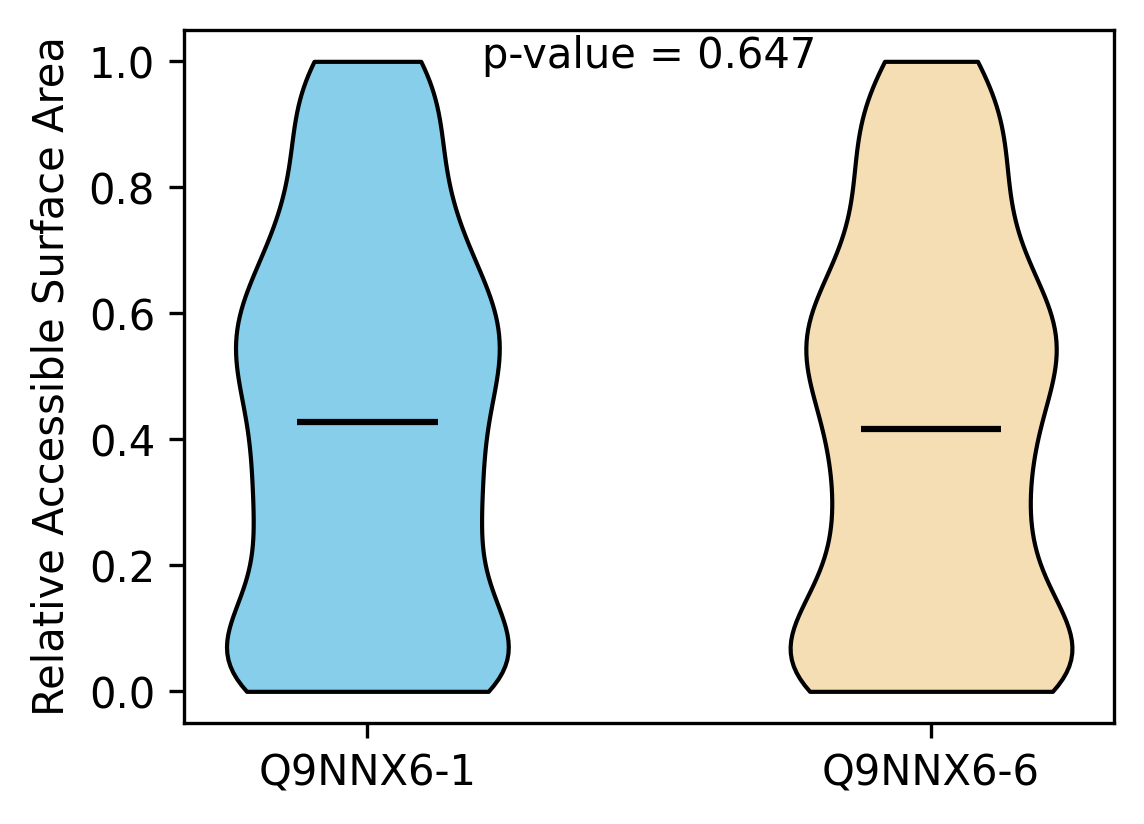
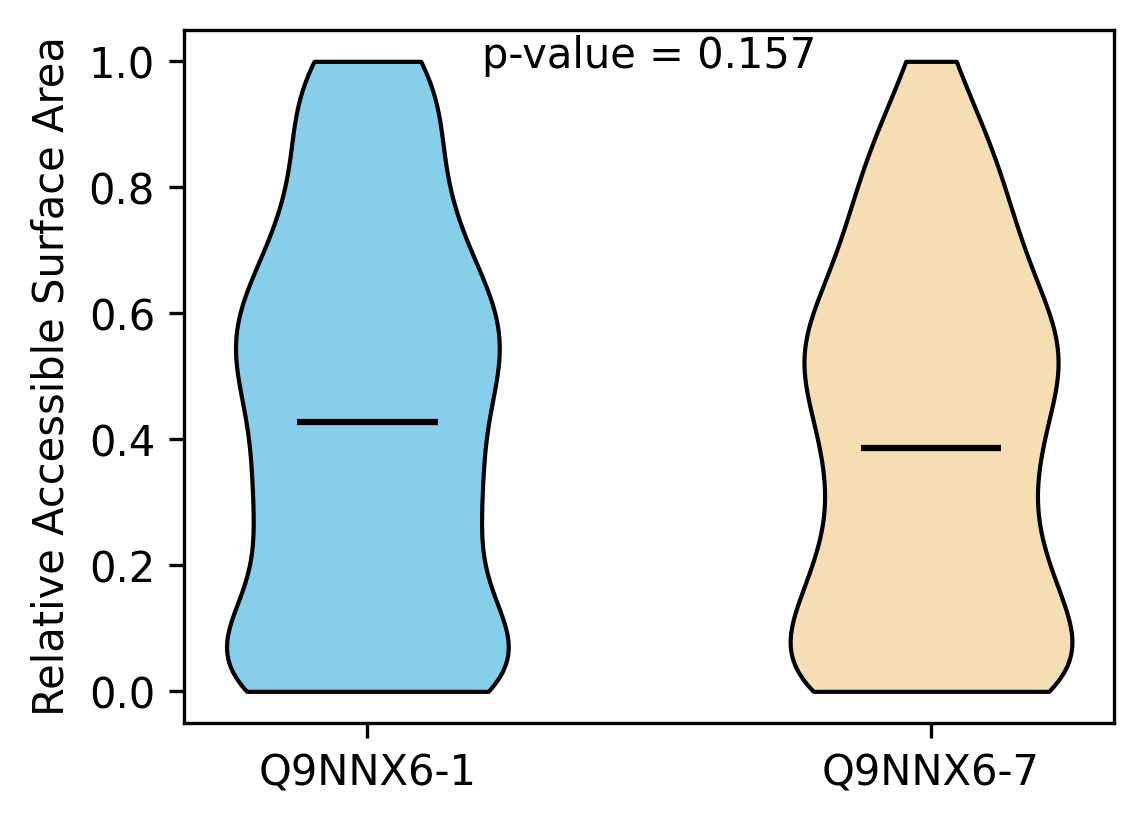
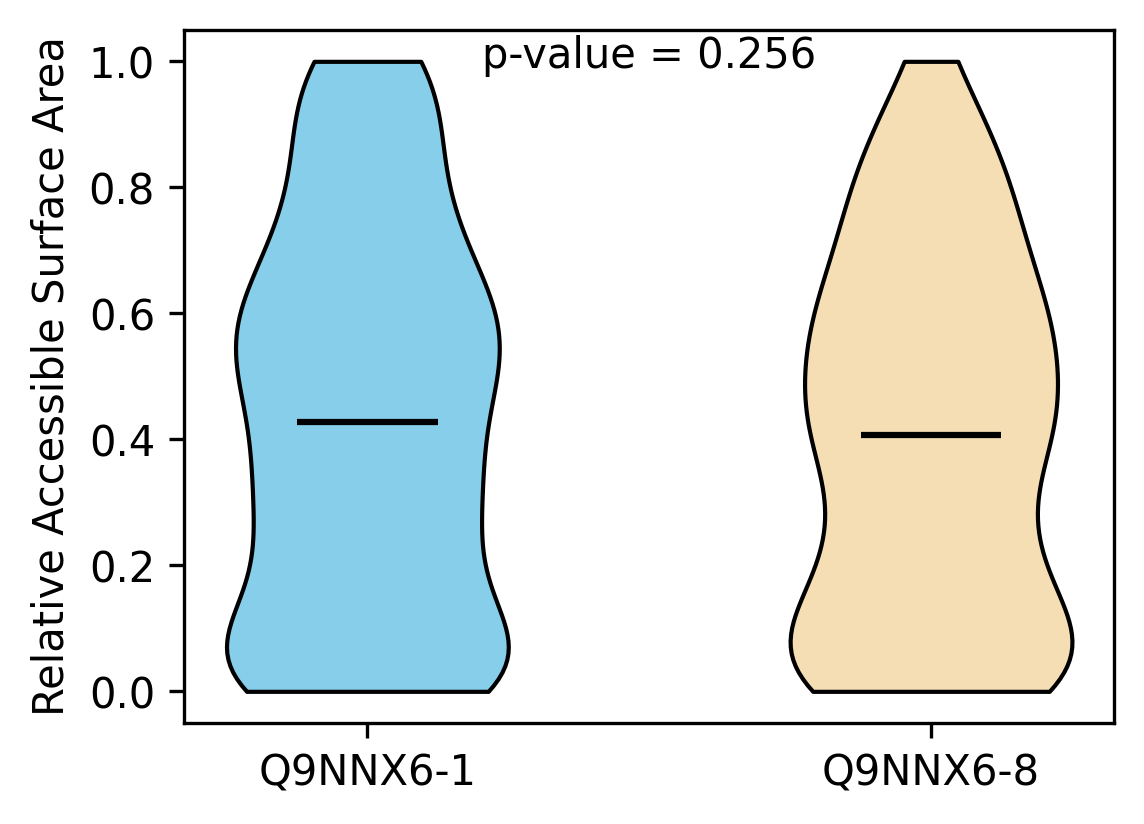
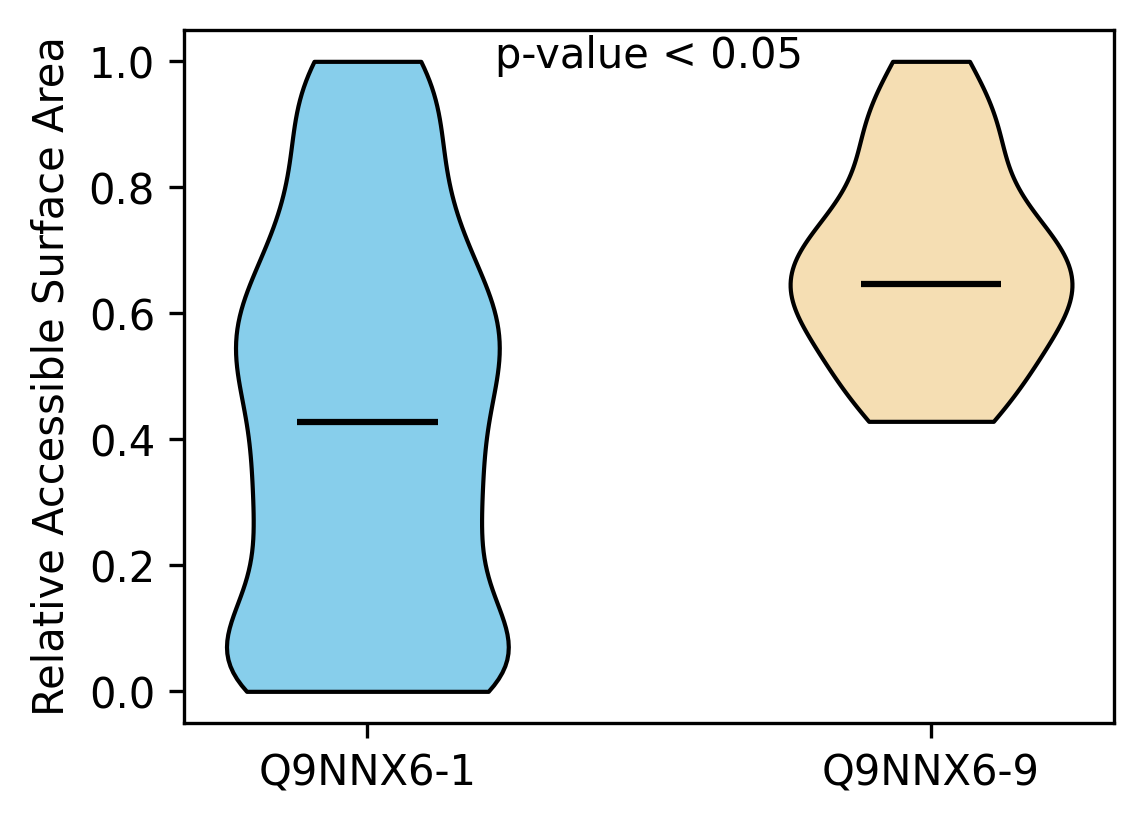
 Protein Feature Comparison of the relative accessible surface area (ASA) among the protiens. Protein Feature Comparison of the relative accessible surface area (ASA) among the protiens. |
Protein-Protein Interaction |
 Interactors from UniProt. Interactors from UniProt. |
| Accession_id | Subsection | Start | End | Funcitonal feature | Splicing information |
 Interactors from STRING. Interactors from STRING. |
| Gene name | Interactors |
Related Drugs to CD209 |
 Drugs targeting this gene/protein. Drugs targeting this gene/protein. (DrugBank) |
| UniProt accession | Gene name | DrugBank ID | Drug name | Drug group | Actions |
Related Diseases to CD209 |
 Previous studies relating to the alternative splicing of CD209 and disease information from the MeSH term (PubMed) Previous studies relating to the alternative splicing of CD209 and disease information from the MeSH term (PubMed) |
| Gene | PMID | Title | Abstract | MeSH ID | MeSH term |
| CD209 | 14603101 | DC-SIGN points the way to a novel mechanism for HIV-1 transmission. | "Dendritic cell (DC)-specific intercellular adhesion molecule 3 (ICAM-3) grabbing nonintegrin (DC-SIGN), a recently discovered type II transmembrane protein on DCs with a C-type lectin extracellular domain, is capable of binding ICAM-3 on resting T cells in the secondary lymphoid organs, providing the initial contact between these cells during the establishment of cell-mediated immunity. DC-SIGN also binds the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp120 but does not function as a receptor for viral entry into DCs. Instead, DC-SIGN allows DCs in the peripheral mucosa to carry HIV-1 through the lymphatics in a ""Trojan horse"" fashion, where it is eventually delivered to the T cells. Also, the period of infectivity of HIV-1 is increased by several days as a result of DC-SIGN-gp120 binding, allowing for efficient trans-infection of T cells on DC arrival. The discovery of a cluster of related genes colocalized with DC-SIGN on chromosome 19p13.2-3, all displaying complex alternative splicing patterns, has led to a reexamination of the mechanisms underlying both the interactions between antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and T cells and the pathogenesis of HIV-1 infection." | D015658 | HIV Infections |
Clinically important variants in CD209 |
 (ClinVar, 04/20/2024) (ClinVar, 04/20/2024) |
| accession_id | uniprot_id | gene_name | Type | Variant | Clinical_significance |
|
|